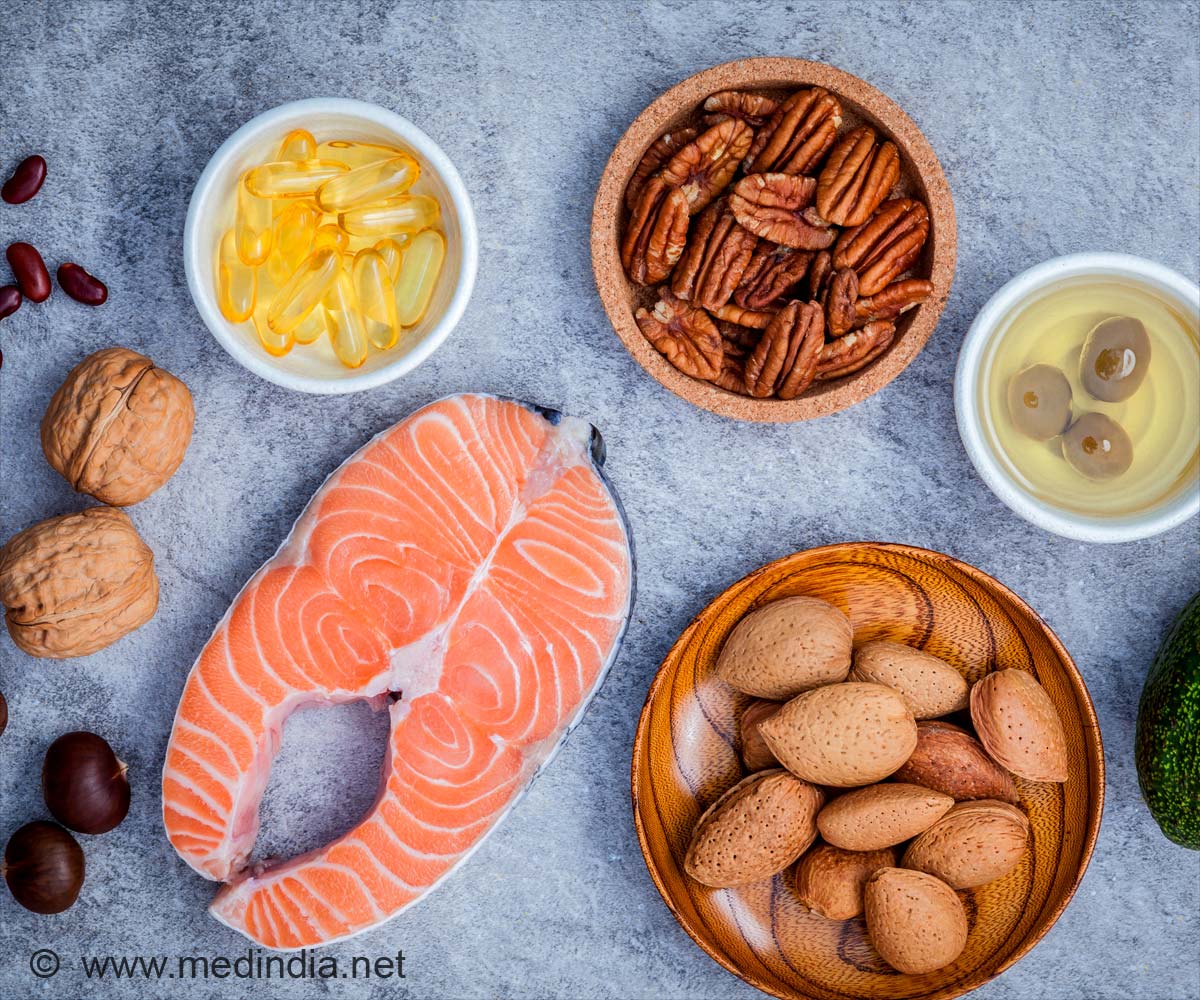
Improve heart health by choosing healthy fats from nuts, avocados, and oils, and avoid eating processed foods and fatty meats.

- Healthy fats support body functions, while unhealthy fats increase health risks
- Excess fat can lead to weight gain and health issues
- Replacing unhealthy fat intake with healthy fats improves health
Fats explained
Go to source).
Healthy vs. Unhealthy Fats
Fats are vital for the body as they provide energy to absorb fat-soluble- Monosaturated fats
- Polyunsaturated fats
- Saturated fats
- Trans fats
Cholesterol is classified into high-density lipoprotein (HDL; good cholesterol) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL; bad cholesterol). Our body requires HDL at high levels and low levels of LDL.
Types of Fat in Our Body
There are three types of fats in our body, each identified by their color as they perform specific functions. They are:- White fat: Most of the fat in our body is white fat. They store energy in different places around the body. It also protects our organs by acting as an insulation. However, too much white fat can lead to obesity.
- Brown Fat: Brown fat stores energy and burns that energy to regulate the body temperature. It is present at a smaller amount than the white fat. Brown fat burns calories and produces heat before the body starts shivering. It helps in regulating fat and sugar metabolism.
- Beige fat: It is a combination of white and brown fat cells. They regulate body temperature by converting white fat cells to brown.
Balanced Diet for a Healthy Body
Excess fat than the required amount will be stored as body fat. Because body fat is required for physical activity and other functions. However, too much body fat can increase the risk of developing heart and circulatory diseases. It can also cause joint pain, make us feel tired, and snore while sleeping.Healthy fats - monosaturated and polyunsaturated fats should be consumed in small amounts. Foods that are rich in healthy fats are nuts, olives, avocados, fish, sunflower seeds, and vegetable oils like rapeseed and olive. Fish are an important source of omega-3 and omega-6 essential fatty acids.
Unhealthy fats - saturated and trans fats should be avoided are replaced with healthy fat foods. Unhealthy fats are obtained from fatty meats, fast food, palm oil, biscuits, and cakes.
How Much Fat Should We Eat Daily?
The majority of people living in the UK eat more saturated fats. According to the UK government's recommendations:- Men should consume less than 30g of saturated fat per day
- Women should consume less than 20g of saturated fat per day
- Both men and women should have less than 5g of trans fat per day
- Children should consume less unhealthy fats than adults
Foods and drinks labeled as low-fat are not alternative options for food with more fat content. Food or drink labeled as:
- ‘lite’, ‘light’ or ‘lighter’, have at least 30 percent less fat than the original product
- ‘low fat’ or ‘reduced fat’, have less than 3g of fat per 100g and the fat content will be labeled in colored green.
Simple Tips to Reduce Unhealthy Fats in Our Diet
Easy tips to reduce unhealthy fat consumption are:- Cook food with vegetable oils like olive, rapeseed, and sunflower oil.
- Avoid eating processed meats like hamburgers and sausages. Instead, choose lean meat like skinless chicken, turkey, and fish.
- Consume plant-based proteins like lentils, beans, or Quorn.
- Use vegetable oils and nuts for sandwich spread. Replace hard cheese and processed meat with oily fish, avocado, and lettuce.
- Measure the amount of oil with a teaspoon before using. Spray bottles are another alternative.
- Eat unsalted nuts and fruit instead of baked foods like biscuits and cakes.
- Consume semi-skimmed, skimmed, or 1% milk. There are other healthier options like almond milk, soya milk, oat milk, and cashew milk that are plant-based.
- Use low-fat cheese like feta, mozzarella, half-fat cheddar, edam, and ricotta instead of halloumi and cheddar.
- Fats explained - (https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/support/healthy-living/healthy-eating/fats-explained)
Source-Medindia