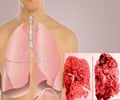
A recent study has suggested that consuming vitamin D can actually have a beneficial effect on the lung, especially in smokers.

Lead author Nancy E. Lange, MD, MPH, of the Channing Laboratory, Brigham and Women's Hospital said, "We examined the relationship between vitamin D deficiency, smoking, lung function, and the rate of lung function decline over a 20 year period in a cohort of 626 adult white men from the Normative Aging Study." "We found that vitamin D sufficiency (defined as serum vitamin D levels of >20 ng/ml) had a protective effect on lung function and the rate of lung function decline in smokers”, she claimed
The findings were published online in the American Thoracic Society's American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.
During the study, vitamin D levels were evaluated three times between 1984 and 2003, and the lung function was assessed using spirometry.
In subjects who were vitamin D deficient, for each one unit increase in pack-years of tobacco smoking, mean forced expiratory volume for one second (FEV1) was 12 ml lower, in comparison to the mean reduction of 6.5 ml among non- vitamin D deficient subjects. Interestingly, no significant effect of vitamin D levels on lung function, or its decline, was observed in the overall study cohort involving smokers and non-smokers.
These results show that vitamin D might modify the damaging effects of smoking on lung function and this may be due to the vitamin’s anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties.
"If these results can be replicated in other studies, they could be of great public health importance," Dr. Lange remarked. "Future research should also examine whether vitamin D protects against lung damage from other sources, such as air pollution," she suggested.
Source-Medindia