Understand how metabolic-bariatric surgery reduces pancreatic cancer risk in obese diabetic patients, offering a significant breakthrough in cancer prevention.

- Obesity is a chronic condition affecting one in eight people
- Obesity and type 2 diabetes increase the risk of pancreatic cancer
- Metabolic-bariatric surgery is known to reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer in obese diabetic patients
Metabolic-Bariatric Surgery Reduces Pancreatic Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis of Over 3.7 Million Adults, Independent of Type 2 Diabetes Status
Go to source).
Metabolic-Bariatric #surgery reduces the risk of #pancreatic_cancer by 54% in obese patients. #medindia’
Link Between Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity and Pancreatic Cancer
Obesity increases the risk of heart diseases, diabetes, bone diseases and fertility issues. Insulin resistance and high cholesterol are conditions that are associated with obesity which increases the risk of some cancers.One common risk factor for type 2 diabetes is obesity. Diabetes screening is recommended for all obese individuals. Treating obesity is important in type 2 diabetes management.
Obesity and type 2 diabetes increase the risk of developing pancreatic cancer, which is the third most common cause of cancer related deaths and has a low survival rate.
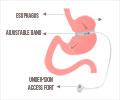
Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Pancreatic Cancer Risk
Metabolic-bariatric surgery (MBS) also known as weightloss surgery, can reduce the risk of obesity related cancers in high risk populations. MBS results in more sustainable weightloss for obese patients compared to standard medical treatment for obesity. It is also effective in treating type 2 diabetes and can lead to type 2 diabetes remission.Weightloss surgery reduces the pancreatic cancer risk by 54% in obese individuals than any other treatment. MBS is effective in treating persons with obesity and type 2 diabetes. MBS reduces the risk of pancreatic cancer by 79% in individuals with obesity and type 2 diabetes and 44% in persons with obesity without type 2 diabetes.
This study was the first to consider the presence of type 2 diabetes in determining the effects of ΜBS on pancreatic cancer risk among the obese population, with or without type 2 diabetes.
With MBS, the fasting insulin level decreases, by altering the molecular signaling, which reduces pancreatic cell proliferation. This surgery reduces the risk of pancreatic cancer in individuals with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Reference:
- Metabolic-Bariatric Surgery Reduces Pancreatic Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis of Over 3.7 Million Adults, Independent of Type 2 Diabetes Status - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39382004/)
Source-Medindia