India is a "sunshine country," yet vitamin D deficiency is widespread among women due to limited sun exposure and vegetarian diets. A little sunlight can go a long way!
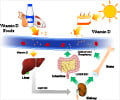
- Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin essential for calcium absorption, which improves bone health
- Animal-based foods offer the bioavailable form of vitamin D, which is easily absorbed by the body
- Women should aim for regular sun exposure during the early morning or late afternoon for safe UVB absorption
Vitamin D Deficiency in India: Prevalence, Causalities and Interventions
Go to source). Vitamin D also contributes to hormone regulation and the proper functioning of the nervous system. Maintaining adequate vitamin D levels is crucial for preventing osteomalacia, osteoporosis and rickets.
Vitamin D deficiency is particularly prevalent in India, where most people follow a vegetarian diet. Over 90% of women in India suffer from vitamin D deficiency. The majority of Indian women have suboptimal vitamin D levels due to dietary patterns, lifestyle factors, and cultural norms that limit sun exposure.
Over 90% of Indian women suffer from vitamin D deficiency due to low sun exposure and vegetarian diets. Regular sunlight and fortified foods can change that! #health #vitaminD #medindia’
Vegetarian Diet and Vitamin D Deficiency
A vegetarian diet lacks sufficient vitamin D, predominantly found in animal-based foods like fish, egg yolks and fortified dairy products. Animal-based foods offer the bioavailable form of vitamin D, which is easily absorbed by the body.As a result, vegetarians may need to depend on fortified foods or supplements to meet their vitamin D requirements. Some plant-based foods, such as UV-exposed mushrooms, contain small amounts of vitamin D2; but the amount is not sufficient.
Without adequate sun exposure or supplements, vegetarians are at a higher risk of vitamin D deficiency.
Other Factors Contributing to Vitamin D Deficiency
India is a sunshine country, yet many individuals, especially women, receive minimal sunlight exposure.Insufficient Sunlight Exposure
:Cultural practices such as wearing full-body or modesty clothing and staying indoors for longer hours, particularly in urban settings, contribute to insufficient vitamin D synthesis. Beauty standards that emphasize lighter skin tones lead to the use of sunscreen and avoidance of sunlight.
Climate Change Factors
:Air pollution in many urban centres limits the number of UVB rays that reach the skin. Increasing cloud covers reduces UV radiation reaching the earth. As temperatures rise, people tend to avoid sun exposure, which increases the risk of vitamin D deficiency.
Hidden Dangers of Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency has many adverse health effects like- Vitamin D is important for calcium absorption. Its deficiency can cause brittle bones, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Postmenopausal women are at higher risk of brittle bones due to hormonal changes.
- Vitamin D deficiency results in impaired muscle strength, fatigue and increased susceptibility to infections. Chronic tiredness and frequent illnesses are common in women with low vitamin D levels.
- During pregnancy, it can increase the risk of gestational diabetes, pre-eclampsia and poor fetal development. Insufficient vitamin D levels during breastfeeding can affect the infant's bone development and immune system.
- It is also associated with an increased risk of heart disease, diabetes and cancer. Low vitamin D levels can exacerbate inflammatory conditions which can lead to autoimmune diseases.
Simple Ways to Boost Your Vitamin D Levels
Women should aim for regular sun exposure during the early morning or late afternoon for safe UVB absorption. Women must be educated on the importance of moderate sun exposure.Incorporate vegetarian-friendly sources like mushrooms (UV-exposed variety) into regular diets and vitamin D-fortified foods like milk and dairy products.
Vitamin D supplements can be useful where dietary intake and sunlight exposure are insufficient. Healthcare providers should recommend vitamin D supplements during winter and pregnancy to maintain optimal vitamin D levels.
Women must engage in outdoor activities to increase sun exposure. Developing workplace policies that encourage breaks in outdoor spaces can be beneficial.
Vitamin D deficiency among Indian women is a pressing health concern influenced by cultural norms, dietary preferences, and environmental factors like air pollution and insufficient sun exposure. Educating women on vitamin D’s role in overall well-being is important to reduce health risks and improve life quality.
Reference:
- Vitamin D Deficiency in India: Prevalence, Causalities and Interventions - (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3942730/)
Source-Medindia