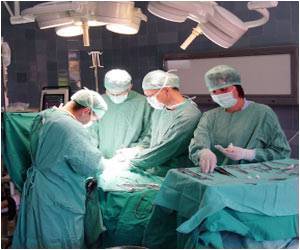
The World Patient Safety Day 2017 is celebrated on the 9th December every year to highlight the importance of patient safety during patient care.
- The World Patient Safety Day 2017 is celebrated on the 9th December every year
- There is an urgent need to improve patient safety by reducing preventable medical errors
- Patients should keep themselves well informed about their illness and the treatment they receive
- One out of 10 patients may be harmed during treatment in a hospital in developed countries
- Fourteen out of every 100 individuals admitted to a hospital suffer from hospital-acquired infections, which is more difficult to treat than community-acquired infections
- The chances that a traveler will be harmed on a flight are much less than in a hospital
- Most adverse effects are caused by surgical procedures, followed by medications and hospital-acquired infections
Medical errors have several impacts – they can affect the patient physically, sometimes affecting the work capacity or even causing death, psychologically as well as financially. Though patients are today protected through various laws, the process of litigation may not be an easy one.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has stressed on the importance of patient safety. Patient safety can be improved through the joint effort of doctors, hospitals as well as patients to improve the quality of care administered to patients:
Doctors: Doctors are primarily responsible for patient safety since they decide on and guide the treatment of the patient. Some measures that doctors can take to reduce medical errors include the following:
- Adequate time should be spent with the patient to ensure that a correct diagnosis is made. After all, the treatment administered to the patient is determined based on the diagnosis
- All prescriptions should be written clearly and in capital letters. Several medications have similar names, but are used for completely different conditions. A clear prescription is necessary so that there are no errors while dispensing the medications
- Medications should be prescribed only as needed, without over prescribing. Too many medications can interact with each other and only add to the adverse effects. The patient should be properly instructed about precautions to be taken while taking the medications to ensure optimal efficacy and minimal side effects
- The prevention of infection in hospitals is extremely important. Regular hand washing by the hospital staff is the simplest measure that can reduce infections to a large extent. Proper sterilization of the equipment, the use of only disposable syringes, the maintenance of cleanliness and the segregation of high-risk individuals can help to reduce the spread of infection among patients
- Proper handovers should be given during the change of staff during shifts
- Data regarding medical errors should be obtained and analyzed regularly so that they can be avoided in the future
- The patient should seek information about the illness and should clear any doubt with the doctor. If the doubt persists, they should seek a second opinion. They should report any side effects to the prescribing doctor at the earliest
- The patients should inform the doctor about any allergy or any disease condition that they may be suffering from or other medications that they may be taking. This would help the doctor decide on the most appropriate medication for the particular patient.
References:
- 10 facts on patient safety - (http://www.who.int/features/factfiles/patient_safety/en/)
- World Alliance for Patient Safety - (http://www.who.int/patientsafety/en/brochure_final.pdf)