Hearing loss is linked to increased cognitive decline with age. However, the impact of mild hearing loss may be reduced by higher education, reveals a new study.
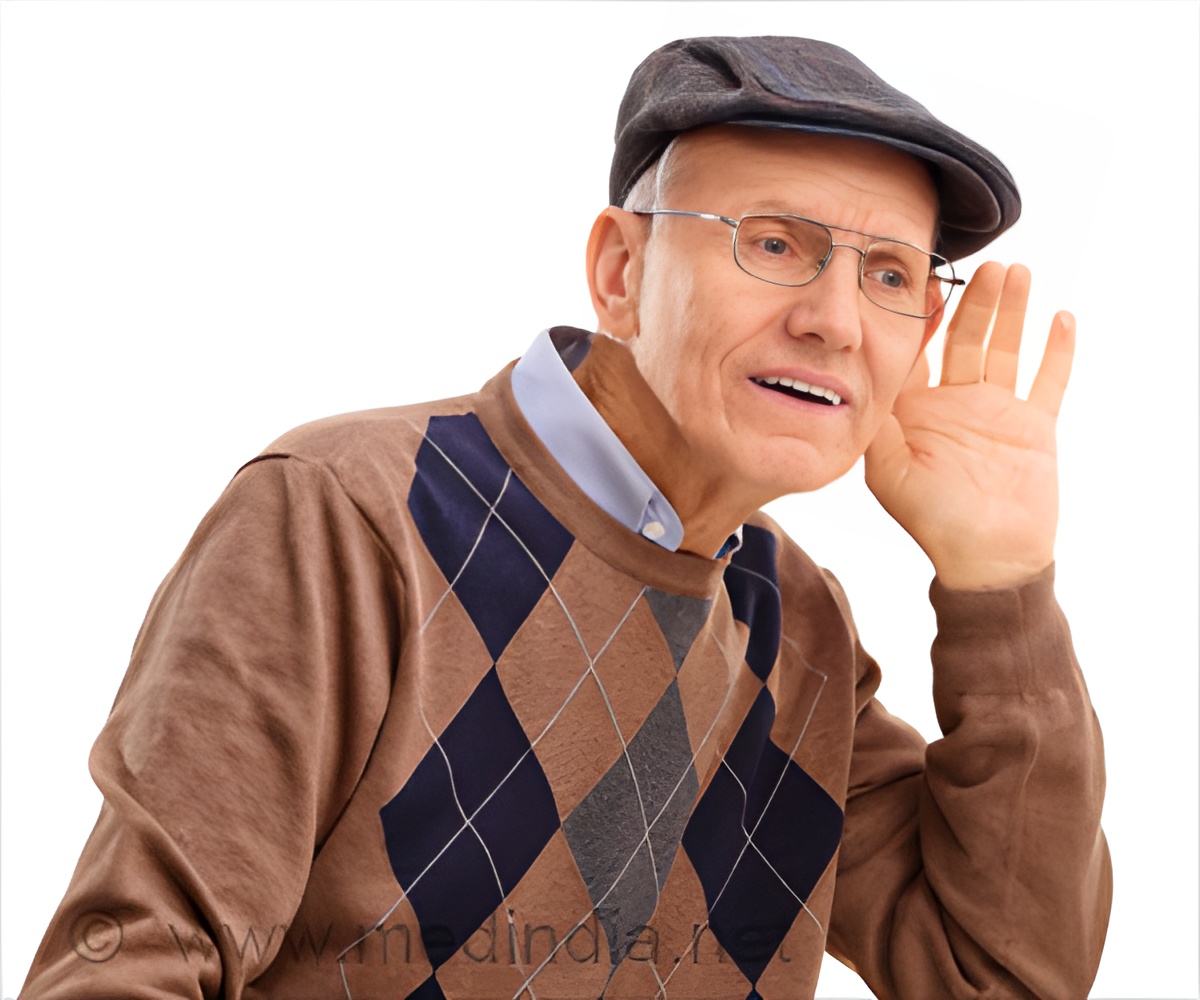

‘Hearing loss is associated with increased cognitive decline with age. However, the impact of mild hearing loss may be reduced by higher education.’
Read More..




The findings suggest that those with more serious hearing impairment had worse performance at the initial visit on a pair of commonly used cognitive assessment tests. Read More..
However, the association of mild hearing impairment with the rate of cognitive decline was modified by education, said the researchers at the University of California, San Diego.
"We surmise that higher education may provide sufficient cognitive reserve to counter the effects of mild hearing loss, but not enough to overcome effects of more severe hearing impairment," said senior author Linda K. McEvoy, Professor at the varsity.
For the study, the research team tracked 1,164 participants with a mean age 73.5 years of whom 64 percent were women.
All had undergone assessments for hearing accuracy and cognitive function between 1992 and 1996 and had up to five subsequent cognitive assessments at approximately four-year intervals. None used a hearing aid.
Advertisement
The team said that mild hearing impairment was associated with a steeper decline among study participants without a college education, but not among those with higher education.
Advertisement
Moderate-to-severe hearing impairment was associated with steeper cognitive decline regardless of education level, the researchers said.
Source-IANS