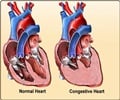
Stem cell therapy for heart failure was safe with no adverse effects and significant improvement in the hearts ability to pump blood.
‘Umbilical cord-derived stem cells are easily accessible, widely available and are unlikely to cause immune complications and free of the ethical concerns for heart failure patients.’





In this trial, 30 patients, ages 18 to 75, with stable heart failure receiving optimal drug therapy underwent intravenous infusions with either umbilical cord-derived stem cells or placebo. The umbilical cords were obtained from full-term human placentas from healthy donors by cesarean section after informed consent. Compared to the placebo treatment, the stem cell therapy:
- showed sustained and significant improvement in the hearts ability to pump blood in the year following treatment
- resulted in greater improvements on measures of daily functional status and quality of life
- was safe with no adverse effects or development of alloantibodies, a common immune complication in patients receiving organ transplants or blood transfusions.
"Standard drug-based regimens can be suboptimal in controlling heart failure, and patients often have to progress to more invasive therapies such as mechanical ventricular assist devices and heart transplantation," said lead study author Jorge Bartolucci M.D., a cardiologist from Cells for Cells and professor at the Universidad de los Andes.
Heart failure, marked by the heart muscle's inability to pump blood efficiently, affects some 37 million people worldwide. Despite medical advances, half of patients diagnosed with heart failure will die within five years of diagnosis, according to Figueroa. If affirmed in larger studies, these findings could provide a promising new treatment option for a condition that currently has few.
Advertisement