Scientists have revealed that mutations in the DNA of hepatitis B virus (HBV) might help predict which patients are at increased risk of developing liver cancer.
Scientists from Second Military Medical University in Shanghai have revealed that mutations in the DNA of hepatitis B virus (HBV) might help predict which patients are at increased risk of developing liver cancer.
HBV infection is a known cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer.During the research, the team analysed 43 studies with a total of 11,582 HBV-infected participants, of whom 2,801 had HCC.
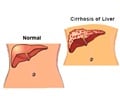
They found that certain mutations were associated with development of HCC, and more prevalent as chronic HBV infection progressed from the asymptomatic state to liver cirrhosis or HCC.
"Frequent examination of patients with chronic HBV infections for the presence of these mutations may be useful for identifying which patients require preventive antiviral treatment and for the prediction of HCC," wrote the authors.
The study appears in Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Source-ANI
SRM