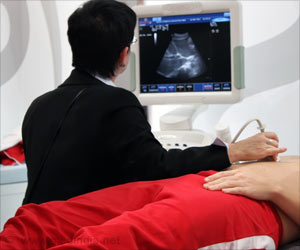
Suffering from chronic intestinal disorders? Here is why the the body’s immune system is affected.
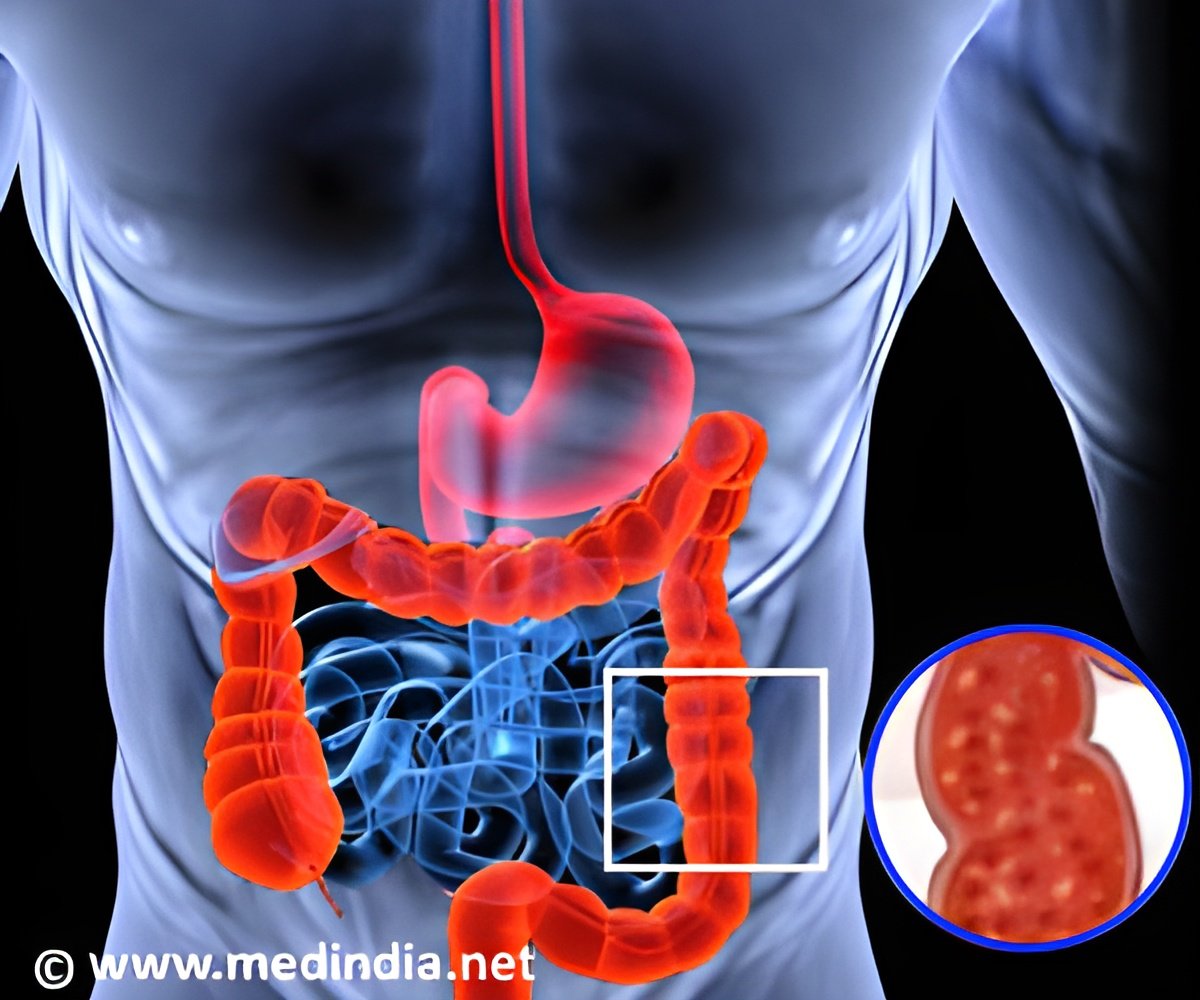
"With the help of our cooperation partners, we were able to demonstrate that the level of the Bcl-3 protein, which also plays a role in the development of various cancerous diseases, is elevated in the intestinal tract of colitis patients and is indeed a trigger of the disease," said Dr. Nadine Hovelmeyer, head of the work group at the Mainz-based Institute for Molecular Medicine.
According to the study, Bcl-3 develops its effect on intestinal health through interaction with the so-called regulatory T-cells (Tregs). Their main task is to prevent overreaction of the immune system and to develop a level of tolerance towards the body they serve.
"We were able to demonstrate that Bcl-3 suppresses the activation of Tregs by preventing the necessary genes from being read. Bcl-3 interacts with the transcription factor p50, which is otherwise responsible for activation, and blocks it," shared Dr. Elke Glasmacher, head of the team at the Institute for Diabetes and Obesity in Munich.
Dr. Sonja Reissig, lead author of the publication and research associate at Mainz University Medical Center noted, "Consequentially, the regulatory T-cells remain passive, the immune system is no longer regulated, and inflammatory processes begin to take place. Experiments using various models have revealed that elevated quantities of Bcl-3 cause certain cells to migrate to the intestines, where they trigger a severe inflammatory response."
Dr. Hovelmeyer concluded by saying, "The results represent a major contribution towards our understanding of chronic intestinal inflammation and hopefully over the long-term will help us discover aspects that we can target with new therapies."
Advertisement
The study was published in Journal Nature Communications.
Source-ANI