Mitochondria are cell organelles that play an important role in generating the energy that cells need to survive.
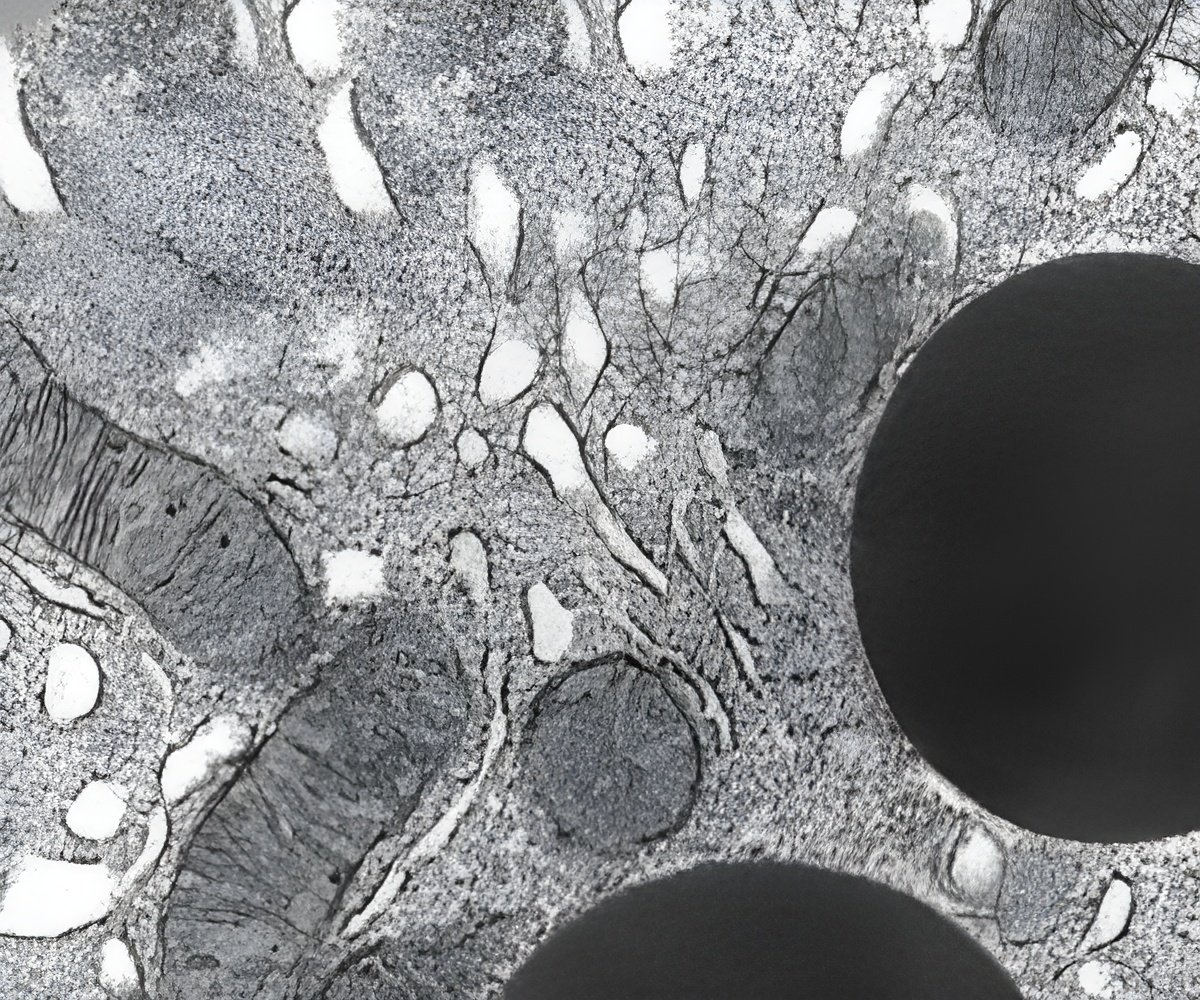
‘The enzyme cps-6 plays a key role in facilitating the self-destruction of paternal mitochondrial DNA, which explains the reason for maternal inheritance of mitochondria.’





The findings showed that a gene CPS-6 serves as a paternal mitochondrial factor that is critical for its degradation.Further, the enzyme that CPS-6 encodes first breaks down the interior membrane of the paternal mitochondria before moving to the space within the inner membrane to breakdown mitochondrial DNA.
CPS-6 plays a key role in initiating the self-destruction of paternal sperm, which likely benefits the embryo.
Delayed removal of paternal mitochondria causes increased embryonic lethality, demonstrating that paternal mitochondrial elimination is important for normal animal development, the researchers explained.
Shortly after a sperm penetrates an egg during fertilisation, the sperm's mitochondria are degraded while the egg's mitochondria persist.
Advertisement
For the study, the team analysed sperm mitochondria or paternal mitochondria in Caenorhabditis elegans -- a type of roundworm -- during early stages of development.
Advertisement