High vitamin D levels in patients with Parkinson's disease may delay or prevent the onset of cognitive impairment and depression, reveals study.
"About 30 percent of persons with PD suffer from cognitive impairment and dementia, and dementia is associated with nursing home placement and shortened life expectancy," Amie L. Peterson, MD, of the Oregon Health and Sciences University, said.
"We know mild cognitive impairment may predict the future development of dementia. Intervening in the development of dementia has the potential to improve morbidity and mortality in persons with PD," Peterson said.
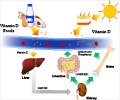
In this analysis, which was an add-on study to an ongoing longitudinal study of neuropsychiatric function in people with PD, patients were given a battery of tests measuring global cognitive function, verbal memory, semantic verbal fluency, executive function, and depression. On the same day, serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels were measured.
Of the 286 subjects, 61 were considered to be demented by a consensus panel based on the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of the American Psychiatric Association (4th edition) and 225 were not demented.
For the entire group, significant negative associations were found between vitamin D levels and disease severity, as measured both by the Hoehn and Yahr Scale and the United Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale motor section. Mean vitamin D3 levels were higher in those who were not demented, although the differences did not reach statistical significance.
Advertisement
"The fact that the relationship between vitamin D concentration and cognitive performance seemed more robust in the non-demented subset suggests that earlier intervention before dementia is present may be more effective," Dr. Peterson added.
Advertisement
Source-ANI