In acne treatment it is essential to recognize that oral/topical antibiotics have limited effectiveness for non-inflammatory lesions.
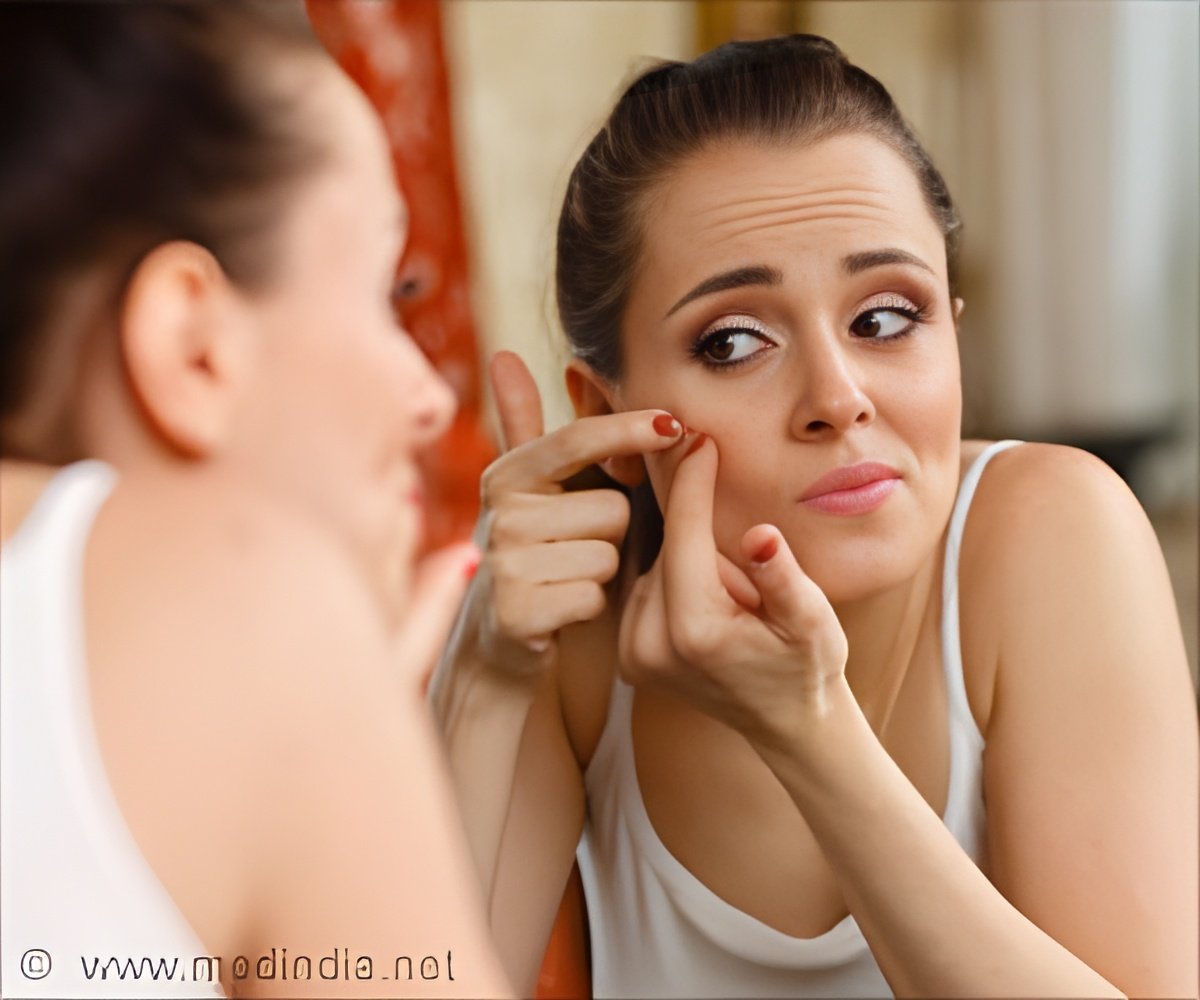

Comparative Efficacy of Pharmacological Treatments for Acne Vulgaris
Go to source). Another triple therapy consisting of an oral antibiotic, a topical retinoid, and BPO also showed substantial efficacy. Among monotherapies, antibiotics or topical retinoids exhibited comparable effectiveness for inflammatory lesions, while antibiotics showed less impact on non-inflammatory lesions.
Understanding Acne
Acne is a common skin disease with an estimated global presence of 9.4% and an annual cost of $3 billion in the United States (2✔ ✔Trusted SourceAcne clinical guideline
Go to source). Although guidelines that recommend medications are generally supported by high-quality, randomized controlled trials, research is lacking on the efficacy of certain medications, particularly when comparing treatment options that have markedly inconsistent drug prescribing patterns among countries and among prescriber specialties.
‘When it comes to combating acne and achieving clearer skin, two highly effective treatments have shown promising results: oral isotretinoin and triple topical therapy. ’





Based on a comprehensive meta-analysis of 210 articles, comprising 221 trials and examining 37 interventions involving 65,601 patients, researchers have concluded that oral isotretinoin is the most effective treatment for acne. Following closely behind, triple therapies incorporating a topical retinoid, benzoyl peroxide (BPO) and an antibiotic have shown significant efficacy. For monotherapies, both oral/topical antibiotics and topical retinoids demonstrate comparable effectiveness for inflammatory lesions.
Reference:
- Comparative Efficacy of Pharmacological Treatments for Acne Vulgaris - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37487721/)
- Acne clinical guideline - (https://www.aad.org/member/clinical-quality/guidelines/acne)