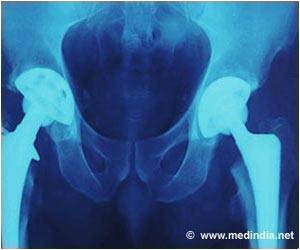
Hip fracture sufferers experienced significantly worse survival at 12-months post-fracture. Hip fracture was a contributory factor in 72% of mortality.
‘Older individuals with hip fracture are 3.5 times more likely to die within 12 months compared to non-injured. The mortality rates were higher in men than women.’





The researchers linked hospital and mortality data from four Australian states. 9748 individuals aged 65 years and older who had a hospital admission with a primary diagnosis of hip fracture in 2009 were matched 1:1 on age, sex, and postcode of residence with a cohort of non-injured individuals selected from the electoral roll. Adjusted mortality rate ratios and attributable risk percent were calculated, and Cox proportional hazard regression was used to examine the effect of risk factors on survival.The researchers found that hip fracture sufferers experienced significantly worse survival at 12-months post-fracture:
Individuals with hip fracture were more than 3.5 times more likely to die within 12 months compared to their non-injured counterparts (mortality rate ratio 3.62 [95%CI 3.23-4.05]).
Hip fracture was likely to be a contributory factor in 72% of mortality within 12 months after the index hospital admission.
Excess mortality risk at 12 months was higher in males than in females, and in the 65-74-year age group compared to older age groups.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert