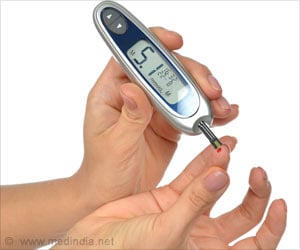
Most hypoglycaemic episodes are generally mild and can be self-treated by eating or drinking glucose tablets, sweets, sugary fizzy drinks or fruit juice.

‘Hypoglycemia is a short-term and avoidable complication of diabetes where the blood sugar of a person with diabetes drops to dangerously low levels.’





According to the study, published in journal The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology, most hypoglycaemic episodes are generally mild and can be self-treated by eating or drinking glucose tablets, sweets, sugary fizzy drinks or fruit juice. But if untreated hypoglycaemic can lead to coma, hospitalisation and death. For the study, the researchers took 1,01,475 cases between 2005 and 2014. The number of admissions for the low blood sugar episodes increased from 7,868 in 2005 to 11,756 in 2010 representing a 49 percent jump and then 10,977 in 2014, up 39 percent in ten years. During the study period, hospital length of stay, mortality and one-month readmissions decreased progressively and consistently.
"Accounting for diabetes prevalence, there was a reduction of admission rates, but this was down to an increase in newly-diagnosed people with Type 2 diabetes who have a much lower risk of hypoglycaemia," said Khunti. The study also highlights on ways developed to help prevent and treat this chronic disease.
Source-IANS