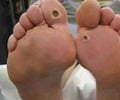
A new study has found that a 50-year-old diabetic may on an average live 8.5 years fewer than a non-diabetic of the same age.

The report, "Profiles of an Aging Society: Diabetes," was released to coincide with National Diabetes Awareness Month in November.
It also found that, compared to older adults without diabetes, those with the disease are less likely to be employed and more likely to have other health problems, such as heart disease, depression, and disabilities that interfere with normal life activities.
Indeed, the figures show a marked increase in the percentage of adults over age 50 with diabetes during the past decade: from 11 percent of non-Hispanic whites in 1998 to 18 percent in 2008, and from 22 percent of non-Hispanic blacks in 1998 to 32 percent in 2008.
The analysis was conducted by Scott M. Lynch, PhD, of the Office of Population Research at Princeton University - using HRS data collected biannually from 1998 through 2008, which included information from more than 20,000 adults over age 50 in 1998.
Source-ANI