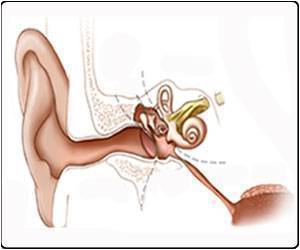
A new study showed that it was possible to use Electroencephalogram (EEG) brain wave signals to determine who a person was paying attention to in a crowded environment.

‘The sound of both things which we pay attention to and ignore are processed similarly but a clear distinction happens in the brain.’





To Understand this scenario, new study has been published in the Journal of Neuroscience.For this study, participants simultaneously listened to two stories but were asked to focus their attention on only one.
Using electroencephalogram (EEG) brainwave recordings, researchers found that the story participants were instructed to pay attention was converted into linguistic units known as phonemes.
Phonemes are units of sound that can distinguish one word from another while the other story was not. That conversion is the first step towards understanding the attended story.
“Sounds need to be recognized as corresponding to specific linguistic categories like phonemes and syllables so that we can ultimately determine what words are being spoken – even if they sound different -- for example, spoken by people with different accents or different voice pitches”, said Co-authors Rochester graduate student Farhin Ahmed, and Emily Teoh of Trinity College, University of Dublin.
Advertisement
The research originated at the 2012 Telluride Neuromorphic Engineering Cognition Workshop and led to the multi-partner institution Cognitively Controlled Hearing Aid project funded by the European Union, which successfully demonstrated a real-time Auditory Attention Decoding system.
Source-Medindia