Brain processes experienced by victims of violence, facilitates the development of action protocols to mitigate the long-term consequences on mental health.
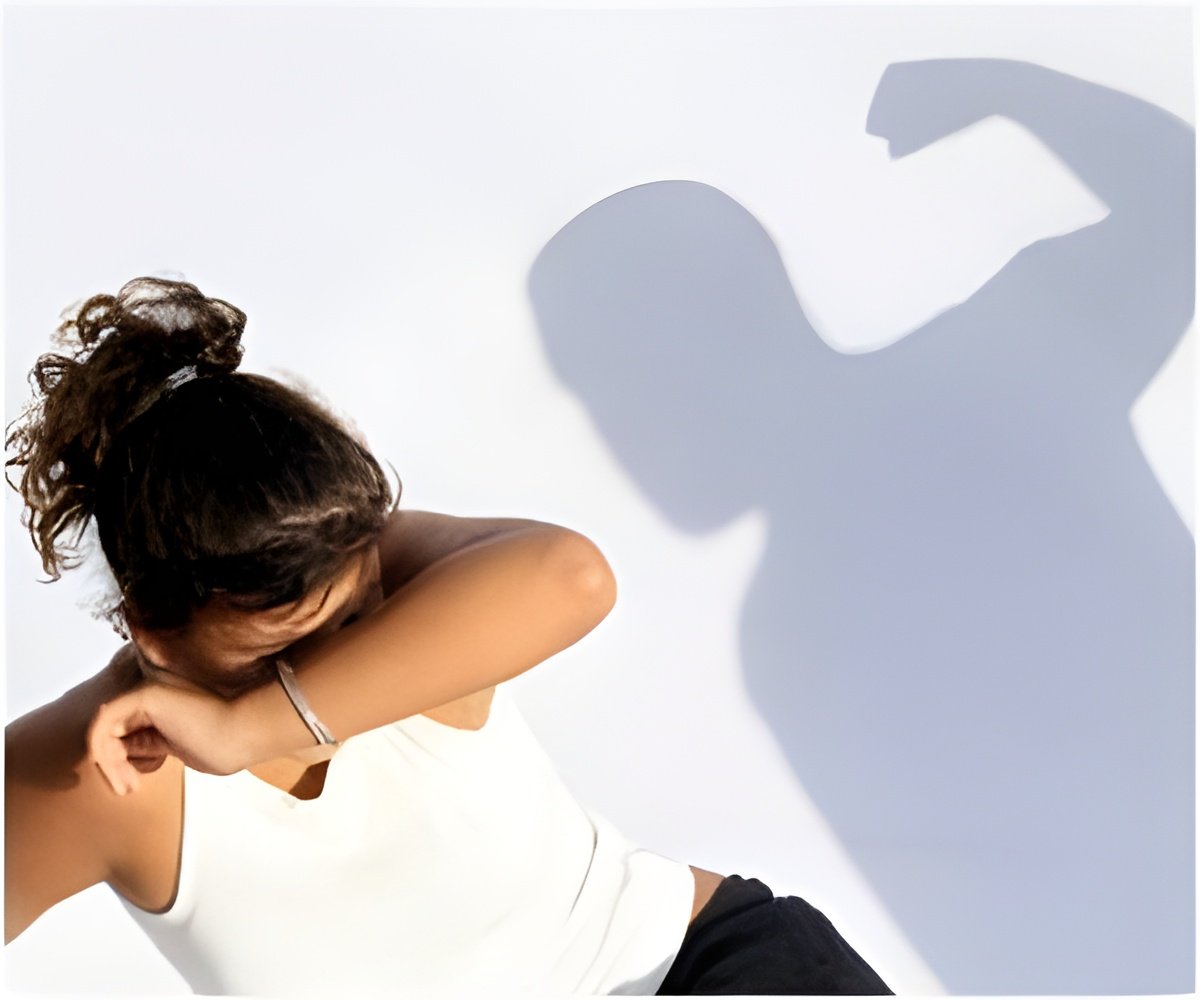

Blunted neurobiological reactivity and attentional bias to threat underlie stress-related disorders in women survivors of intimate partner violence
Go to source). An article coordinated by the Parc Taulí Hospital and the UAB analyses the consequences of this sustained stress over time and studies how it affects both their ability to detect threatening situations and their mental health.
‘Among women, long-term exposure to stress affects biological stress response systems, such as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and the sympathetic nervous system, which can be influenced by their response to danger signals, particularly threatening faces. #violence’





Women who have experienced violence are known to have a two to four times higher risk of depression, anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder, even years after the end of the violent relationship. However, the reason for this increased risk is not known.
Impact of Chronic Stress on Physiological Responses and Facial Expression Detection
An article coordinated by Dr Ximena Goldberg from the Parc Taulí Hospital and Professor Antonio Armario, from the UAB Department of Cell Biology and the UAB Institute of Neurosciences, Physiology and Immunology, evaluates the consequences of this situation of chronic stress on physiological responses to specific stressful situations, as well as on the ability to detect threatening facial expressions.The study involved 105 women (69 victims of gender-based violence and 36 control participants) who took two tests. In the first, the participants were confronted with a standardized stress situation including a simulated job interview and a mathematical calculation. Afterwards, saliva samples were collected to measure their physiological response to acute stress. In a second phase, the women were shown neutral faces or faces with threatening expressions on a screen, and their attention was measured.
The research group, which included professionals from Parc Taulí Hospital, Tel Aviv University, CIBERSAM group G-29 and the UAB, observed that in the attention test, one group of women was much more attentive to threatening faces, following a vigilant attitude pattern, while another group avoided them. Women victims of gender-based violence who followed a vigilant pattern had a higher stress response, particularly with cortisol, than the control group. In contrast, female victims of gender-based violence with an "avoidance" pattern had lower cortisol and α-amylase responses.
Dr. Ximena Golberg, researcher at ISGlobal and Parc Taulí Hospital, and first author of the article, explains that the results allow us to advance in the knowledge of the brain processes experienced by victims of violence, in order to develop better action protocols and minimise the consequences on long-term mental health.
Reference:
- Blunted neurobiological reactivity and attentional bias to threat underlie stress-related disorders in women survivors of intimate partner violence - (https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/psychological-medicine/article/abs/blunted-neurobiological-reactivity-and-attentional-bias-to-threat-underlie-stressrelated-disorders-in-women-survivors-of-intimate-partner-violence/57349C6CAD67FA93A7A0F41F970973A3)