LPC-DHA dietary supplement proves safe and effective in treating acute kidney injury, providing lifelong protection for the kidneys.
Mfsd2a mediated lysolipid transport is important for renal recovery after acute kidney injury
Go to source)
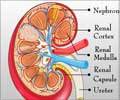
Insights Into Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
A major public health concern, AKI affects an estimated 13.3 million people globally each year and has a mortality rate of 20 to 50 percent depending on the economic status of the country and stage of the disease. One of the main causes of AKI is ischemic reperfusion injury, which occurs when the kidney’s blood supply is restored after a period of restricted blood flow and poor oxygen delivery due to illness, injury or surgical intervention. In particular, it damages a crucial part of the kidney called the S3 proximal tubules that regulate the levels of absorption of water and soluble substances, including salts. “AKI is a serious health problem with limited treatment options,” said Dr Randy Loke, first author of the study and an MD-PhD student with Duke-NUS’ Cardiovascular & Metabolic Disorders (CVMD) Programme. “We sought to understand how these tubules repair themselves and found that the activity of the protein Mfsd2a, which transports LPC-DHA into cells, is a key factor influencing the rate of recovery of kidney function after ischemic reperfusion injury.”Impaired Mfsd2a Levels in Preclinical Models Impede Kidney Injury Recovery
In their study, the researchers discovered that preclinical models with reduced levels of Mfsd2a showed delayed recovery, increased damage and inflammation after kidney injury. LPC-DHA also restored the structure of the S3 proximal tubules, helping them function properly again.‘In preclinical models of acute kidney injury, the administration of omega-3 lipid LPC-DHA resulted in improved kidney function and reduced damage. #kidneydisease’





“While more research is needed, the potential of LPC-DHA as a dietary supplement is exciting for future recipients who have suffered from AKI,” said Professor David Silver, the senior author of the study and Deputy Director of the CVMD Programme. In the next phase, the research team plans to continue investigating the beneficial functions of LPC in the kidney and are aiming to initiate clinical testing of LPC supplements to determine their effectiveness in improving renal function and recovery following AKI in patients.
They also plan to continue their investigations of the protein Mfsd2a to learn more about its role in LPC transport and its involvement in diseases affecting other tissues and organs. Previous research by Prof Silver’s group, with collaborators from other institutions, have already highlighted the significance of the protein’s LPC-transporting activities in diseases of other organs, including the liver, lungs and brain.
Reference:
- Mfsd2a mediated lysolipid transport is important for renal recovery after acute kidney injury - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37467896/)