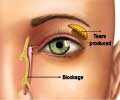
New research highlights the calming effect of chemicals that are found in women's tears on men.

A chemical signal in human female tears lowers aggression in males
Go to source). Male aggression in rodents is known to be blocked when they smell female tears. This is an example of social chemosignaling, a process common in animals but less common—or less understood—in humans.
‘Chemicals in women's tears have a calming effect on men by reducing aggression-related brain activity, thereby leading to less aggressive behavior.
#tears, #women, #aggression, #men
’





To determine whether tears have the same effect in people, the researchers exposed a group of men to either women’s emotional tears or saline while they played a two-person game. The game was designed to elicit aggressive behavior against the other player, whom the men were led to believe was cheating. When given the opportunity, the men could get revenge on the other player by causing them to lose money.
The men did not know what they were sniffing and could not distinguish between the tears and the saline, which were both odorless.
Mind-Altering Tears
Revenge-seeking aggressive behavior during the game dropped more than 40% after the men sniffed women’s emotional tears.When repeated in an MRI scanner, functional imaging showed two aggression-related brain regions—the prefrontal cortex and anterior insula—that became more active when the men were provoked during the game, but did not become as active in the same situations when the men were sniffing the tears.
Individually, the greater the difference in this brain activity, the less often the player took revenge during the game.
Advertisement
The authors add, “We found that just like in mice, human tears contain a chemical signal that blocks conspecific male aggression. This goes against the notion that emotional tears are uniquely human.”
Advertisement
- A chemical signal in human female tears lowers aggression in males - (https://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002442)
Source-Eurekalert