Fist study of its kind to examine whether maternal immune activation is linked to poorer outcomes in children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD).

‘Immune-mediated subtype in ASD may be driven by changes in cytokine, chemokine or antibody levels in the mother and/or child.’





Maternal immune activation (MIA) has been highlighted as a factor that might increase the risk of ASD; however, this new study is believed to be the first to examine whether MIA is linked to poorer outcomes in children with ASD. MIA is defined as an active immune response during pregnancy that can be triggered by an external event such as infection or autoimmune disorders. The mechanisms by which MIA increases the risk of ASD are largely unknown but research suggests that an immune-mediated subtype in ASD may be driven by changes in cytokine, chemokine or antibody levels in the mother and/or child.
The researchers say the identification of an immune system-mediated subtype in ASD driven by MIA and immune biomarkers would enable more streamlined diagnosis and management in clinical settings.
Preclinical animal models have shown that immune activation during pregnancy causes ASD-like phenotypes in offspring, which supports the MIA hypothesis.
Children recruited to the study were administered the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule-Generic (ADOS-G) that uses simple activities and questions designed to prompt and observe communication, social and stereotyped behaviours relevant to the diagnosis of ASD.
Advertisement
A primary caregiver completed a family history questionnaire, which included a medical history including any diagnosed illnesses or chronic conditions.
Advertisement
Natalie Pollard said trying to understand why her eldest son, Ethan, 7, has autism was a "long journey", but the findings were a positive step.
The University of Sydney academic from Dural doesn't suffer from asthma and allergies, and her two younger sons do not have autism.
"I knew something wasn't quite right early on, and his development was slower and he would scream for hours," she said.
"As a mum, I think the findings are great, because we need more information out there and it could potentially help solve the puzzle of autism, which is multi-factorial."
Results
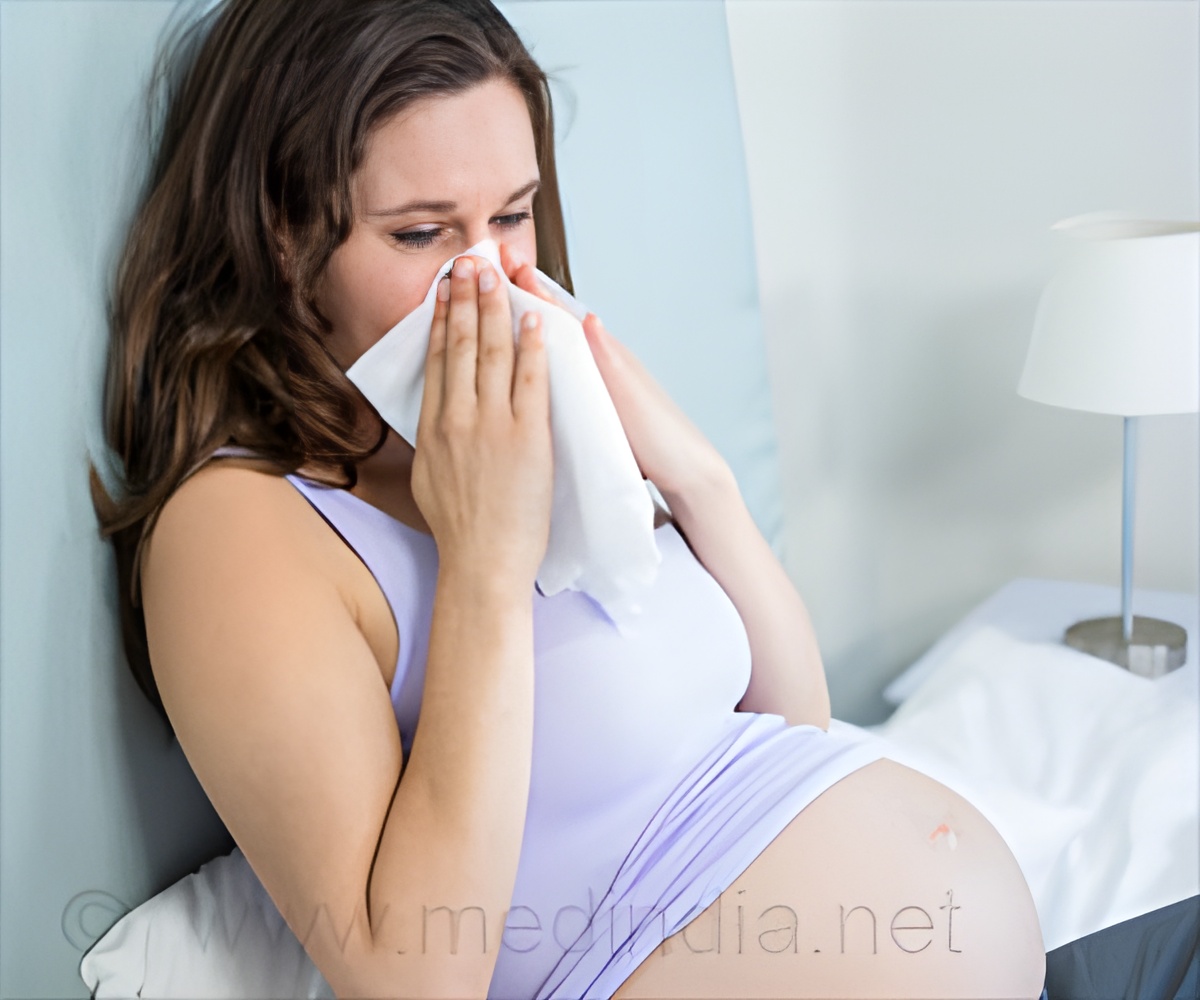
• A history of allergies or asthma in the mother was associated with increased severity of social symptoms
• A history of autoimmune conditions in the mother was not associated with increased symptom severity
"Our results build on existing research by showing an associated between maternal immune activation caused by asthma and allergies and ASD symptom severity in children with ASD, said Shrujna Patel, a University of Sydney PhD candidate who led the study with colleagues at the Brain and Mind Centre, Children's Hospital Westmead, Macquarie University and the Telethon Kids Institute.
"Children of mothers who reported a history of immune activation had significantly higher Social Responsiveness Scale total scores, suggesting they had more severe caregiver-reported deficits," she said.
"Specifically, they had higher scores on cognition and mannerisms subscales, suggesting they had more difficulty understanding social situations and displayed more restricted behaviours or unusual interests."
The researchers said the identification of an immune system-mediated subtype in ASD driven by MIA and immune biomarkers would enable more streamlined diagnosis and management in clinical settings.
The findings also support the investigation of biomarkers in this sub-group and present potential new targets for immune-modulating drug therapies.
Source-Eurekalert