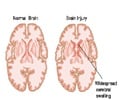
Elevated markers of brain injury reported as a result of clinically asymptomatic high-acceleration head impacts in high-school football athletes, revealed research.
‘Elevated markers of brain injury reported as a result of clinically asymptomatic high-acceleration head impacts in high-school football athletes.’





In this paper, the authors used helmet-based accelerometers and measurements of serum biomarkers of traumatic brain injury (TBI) to examine the effects of high-acceleration head impacts (HHIs) and to specifically answer the following questions: * Would HHIs result in high serum levels of biomarkers of TBI, even in the absence of clinical symptoms of concussion? * What would be the longitudinal profile of TBI markers in athletes over the course of a high-school football season? Sixteen high-school varsity football players wore helmet-based accelerators that measured and recorded all head impact data during practices and games throughout the 2016 football season. An HHI was defined as a hit to the head involving both linear acceleration greater than 95g and rotational acceleration greater than 3760 rad/second2. During the entire football season a total of 7,756 head impacts were recorded, of which only 11 (0.001%) met the criteria of an HHI. Six athletes experienced one or more HHIs at some point during the season; five other athletes who did not experience an HHI served as controls.
Blood samples were collected from players at the beginning of the season (16 players), at the end of a game in which an HHI occurred (6 players), following the final game (5 players used as controls for the 6 players with HHI), and after the end of the season (12 players in whom there was no diagnosis of concussion and no discrepancy in biomarker analyses). The athletes' blood samples were tested for serum levels of the following TBI markers: tau, ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1), neurofilament light protein, glial fibrillary acidic protein, and spectrin breakdown products.
The authors' review of TBI biomarker levels showed statistically significant increases in serum levels of both tau and UCH-L1 after an athlete sustained a single HHI, compared with levels in athletes who did not experience an HHI. When the authors examined TBI biomarker levels over the course of the season, they also found statistically significant increases in post-season levels of both tau and UCH-L1, compared to pre-season levels, in athletes with no diagnosis of concussion. There were no significant increases in the serum levels of the other TBI biomarkers that were tested.
UCH-L1 is a biomarker of neuronal body injury and tau is a biomarker of axonal injury. In their prospective, observational cohort study, Joseph and colleagues identified an association between increased biomarkers of neuronal and axonal head injury and HHI in high-school varsity football players. In addition, the authors showed an association between increased biomarkers of neuronal and axonal head injury, and athletes who played throughout the course of an entire football season, even those athletes in whom no HHI exposure occurred.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert