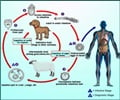
Cholera, viral hepatitis, enteric fever and acute diarrhoeal diseases are the main water borne diseases caused by contamination of water with virus and bacteria.
Outbreak of diseases especially water-borne and vector-borne diseases may occur after floods. Cholera, viral hepatitis, enteric fever and acute diarrhoeal diseases are the main water borne diseases caused by contamination of water with virus and bacteria, whereas diseases caused by mosquitoes, which mainly breed in water, are dengue, malaria, filariasis, viral encephalitis etc.
Health is a State subject and primarily, the State Government is responsible for the management of waterborne and other diseases in wake of the floods. The Government of India supplements the efforts of the State Governments/Union Territories by providing technical support and material supplies to the State Governments on their request or when the extent of the outbreak is beyond the coping abilities of the State. Prior to the onset of monsoon season, guidelines and the action required to be taken by the State Governments for prevention and control of various diseases, which may arise due to floods, are circulated to all the States. These guidelines elaborate on likely public health risks, stepping up of surveillance to detect early warning signs, ensuring safe drinking water and instituting public health measures to prevent outbreak of diseases.The Government of India provides financial assistance to the State affected by natural calamities as per norms of Calamity Relief Fund (CRF) shared by the Centre and the State on 75:25 basis. If the calamity is of severe nature, additional funds are also made available from National Calamity Contingency Fund (NCCF). The requirement of the additional funds is assessed by Ministry of Home Affairs, which is the nodal Ministry for the fund. The CRF and NCCF norms include assistance for provision of medicines, disinfectants, insecticides for prevention and outbreak of epidemics.
In addition, a comprehensive National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP) is implemented through the States for prevention and control of vector borne diseases caused by mosquitoes.
The strategies for control of vector borne diseases include disease management through early case detection and treatment, epidemic preparedness and rapid response. An integrated approach has been initiated with Department of Drinking Water Supply to provide the technical support to monitor the quality of drinking water in different states so as to prevent occurrence of water borne diseases.
The Government of India has also launched an Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme in November 2004, to further strengthen identification of outbreaks of various diseases including water borne and vector borne diseases so that early intervention could be made and occurrence, disability and death due to such diseases could be reduced.
This information was given by the Minister for Health & Family Welfare, Dr. Anbumani Ramadoss in a reply to a question in the Rajya Sabha.
Advertisement
SRM/N