Recent advancements in retinoblastoma treatment have greatly improved the odds of preserving both life and vision in children.

Advancements in super-selective catheterization and drug selection for intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma: a 15-year evolution
Go to source).
15 Years of Progress in Intra-Arterial Chemotherapy for Retinoblastoma
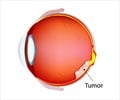
The study, “Advancement in Super-Selective Catheterization and Drug Selection for Intra-Arterial Chemotherapy for Retinoblastoma: A 15-year Evolution,” reviewed how children received intra-arterial chemotherapy (IAC), the gold standard for treating retinoblastoma, by delivering chemotherapy directly to the affected eye. Using IAC helps to minimize the need to remove a patient’s affected eye and maximizes their ability to see after treatment, as well as their potential to survive the cancer.The research team — composed of neurointerventionalists from New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medicine, and ophthalmologic oncologists at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center — reviewed medical records for 571 patients separated into three cohorts five years apart.
The data was evaluated to determine how routes of vascular access to the ophthalmic artery has evolved over time, how many patients have had complications from the procedure, and what combinations of chemotherapy drugs patients have received. Researchers found that, of a total of 2,402 attempted IAC sessions, 2,391 (99.5%) were successful.
Success rates of super-selective catheterizations, where the ophthalmic artery was catheterized directly, also has improved over time; 80% of the earliest procedures were successful compared to 89.2% of the most recent procedures.
Procedure complication rates stayed very low over time at 0.7% for the earliest cohort, 1.1% in the middle cohort and 0.6% in the most recent cohort. In addition, researchers found that more and more children have successfully received a three-chemotherapy combination from 21% of the earliest cohort to 66.7% of the most recent cohort. Finally, the authors proposed a stepwise algorithm to help others maximize direct vascular access to the ophthalmic artery.
“We are proud to share our history of ongoing success in using this minimally invasive method to care for some of our youngest cancer patients,” said Gary Kocharian, MD, Neurosurgery Chief Resident and Endovascular Neurosurgery Fellow at New York-Presbyterian Hospital.
Advertisement
Reference:
- Advancements in super-selective catheterization and drug selection for intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma: a 15-year evolution - (https://jnis.bmj.com/content/16/4/398)