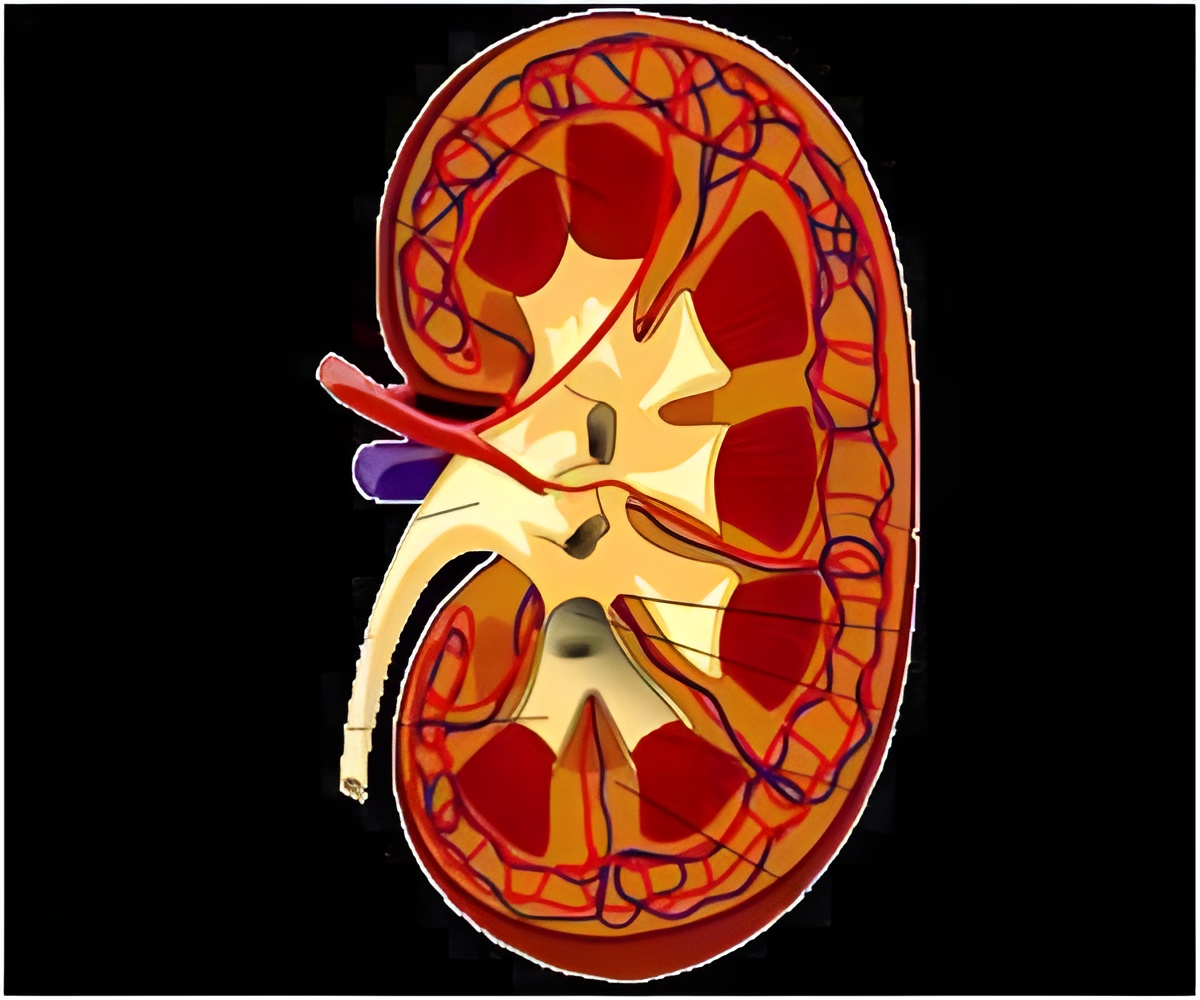
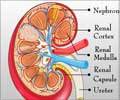
Disparities related to kidney disease may be influenced by perceived racial discrimination, reveals a study that will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2014 November 11Â.
Disparities related to kidney disease may be influenced by perceived racial discrimination, reveals a study that will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2014 November 11-16 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia, PA.
Psychosocial factors such as perceived racial discrimination have been associated with chronic diseases, but little is known about the relationship between perceived racial discrimination and kidney function decline. Researchers led by Angedith Poggi-Burke, MPH, and Deidra Crews, MD, FASN (National Institute on Aging and Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, respectively) studied 1,574 adults with preserved kidney function in the Healthy Aging in Neighborhoods of Diversity across the Life Span (HANDLS) study (Baltimore City, Maryland). The team found that 20% of individuals perceived themselves to have been discriminated against a lot because of their race. Such individuals were more likely to be African American and have a higher educational background, but they were more likely to be living in poverty than those who reported little-to-no perceived discrimination. Additionally, those who perceived a lot of discrimination had higher systolic blood pressure but a lower prevalence of diabetes than those perceiving little-to-no discrimination.
Overall, perceived racial discrimination was linked with greater kidney function decline over 5 years of follow-up that was independent of socio-demographic, lifestyle, and health factors. When analyzed by race and sex, the link between perceived racial discrimination and kidney function decline remained only among African American women. Systolic blood pressure was responsible for 15% of this association.
"Perceived racial discrimination may contribute to disparities in kidney disease and might exert its effect on risk of kidney function decline through stress-related pathways," said Dr. Crews. "This study can serve as a basis for future studies focusing on psychosocial stressors and their potential contributions to the initiation and progression of kidney disease."
Study: "Association of Perceived Racial Discrimination and Kidney Function Decline among African Americans and Whites" (Abstract SA-PO856)
Disclosure information is available at
http://www.asn-online.org/education/kidneyweek/2014/program-faculty.aspx.
ASN Kidney Week 2014, the largest nephrology meeting of its kind, will provide a forum for more than 13,000 professionals to discuss the latest findings in renal research and engage in educational sessions related to advances in the care of patients with kidney and related disorders. Kidney Week 2014 will take place November 11-16, 2014, in Philadelphia, PA. Advertisement
The content of this article does not reflect the views or opinions of The American Society of Nephrology (ASN). Responsibility for the information and views expressed therein lies entirely with the author(s). ASN does not offer medical advice. All content in ASN publications is for informational purposes only, and is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions, or adverse effects. This content should not be used during a medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. Please consult your doctor or other qualified health care provider if you have any questions about a medical condition, or before taking any drug, changing your diet or commencing or discontinuing any course of treatment. Do not ignore or delay obtaining professional medical advice because of information accessed through ASN. Call 911 or your doctor for all medical emergencies.
Founded in 1966, and with more than 15,000 members, the American Society of Nephrology (ASN) leads the fight against kidney disease by educating health professionals, sharing new knowledge, advancing research, and advocating the highest quality care for patients. Advertisement
Source-Newswise