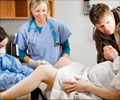
A test for fetal fibronectin can predict whether a pregnant woman is at risk for early labor and delivery. Those at high risk for pre-term births are
A test for fetal fibronectin can predict whether a pregnant woman is at risk for early labor and delivery. Those at high risk for pre-term births are women with previous pre-term deliveries, those with multiple gestation pregnancy, and those who suffer from diabetes and/or hypertension. The current approach for finding whether a woman will go into premature labor is the use of a clinical scoring system, risk classification, and patient presentation; The marker that can identify at-risk women is fetal fibronectin (fFN).A glycoprotein that is secreted by the fetal membrane and found in the choriodecidual junction, fFN is responsible for cellular adhesions. The level of fFN in the woman's cervicovaginal secretions is highly associated with pre-term labor and pre-term delivery. The fFN immunoassay detects concentrations of fetal fibronectin protein in cervicovaginal fluids; the presence of more than 50 ng/mL is considered positive.
The fFN test has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use as an aid in assessing the risk of pre-term delivery during the routine screening of asymptomatic patients from 22-30 weeks' gestation, and for women with symptoms of pre-term labor from 24-35 weeks' gestation. High-risk asymptomatic patients with a low fFN reading may be advised to continue with additional repeat follow-ups, with a repeat of the test if the patient becomes symptomatic.