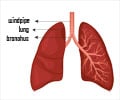
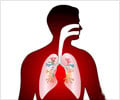
A recent study from Rhode Island Hospital has pointed out that testing patients for possible community-acquired pneumonia due to Legionella needs improvement to enable a more accurate diagnosis.

Legionella is the bacteria that causes Legionnaires' disease, a dangerous and potentially fatal infectious disease. In the Infectious Diseases Society of American (IDSA) and the American Thoracic Society (ATS) community-acquired pneumonia guidelines, testing for the urine antigen of Legionella is recommended for patients with any of the following: severe pneumonia requiring intensive care unit admission, failure of outpatient antibiotics, active alcohol abuse, history of travel within previous two weeks, or pleural effusion.
Leonard Mermel, DO, medical director of the epidemiology and infection control department at Rhode Island Hospital, is the senior author of this retrospective study that identified nearly 4,000 patients with a primary or secondary diagnosis of pneumonia in an 18-month period. Of those patients, 35 percent had a Legionella urine antigen testing or had a Legionella culture performed. In addition, 44 percent of patients who had a bronchoscopy had a specimen sent for Legionella culture and/or had Legionella urine antigen testing. Of the patients with pneumonia due to Legionella, only 22 percent met the IDSA/ATC criteria recommending Legionella testing.
Mermel says, "This single-center study suggests that current recommendations for Legionella testing will result in missed cases. More widespread testing will identify additional cases allowing focused antimicrobial therapy and will alert public health officials of such Legionella cases".
Co-author Brian Hollenbeck, M.D., adds, "Legionella is a severe cause of community- and hospital-acquired pneumonias. We hope that this study will raise awareness of the need for more comprehensive Legionella testing in patients who are hospitalized with pneumonia."
Advertisement