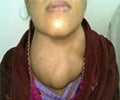
People with certain single nucleotide polymorphisms were significantly more likely to develop cancer in their thyroid, a gland in the throat that controls metabolism, revealed study.
‘Genetic susceptibilities play an important role in cell phone use and the risk of developing thyroid cancer and could help to identify subgroups who are potentially at risk.’





Cell phone users with SNPs in four of the genes studied were more than two times likely to develop cancer. The researchers examined a total of 176 genes and identified 10 SNPs that appear to increase the risk of thyroid cancer among cell phone users. Published in the journal Environmental Research, the study is believed to be the first to examine the combined influence of genetic susceptibility and cell phone use in relation to thyroid cancer.
"Our study provides evidence that genetic susceptibility influences the relationship between cell phone use and thyroid cancer," said Yawei Zhang, M.D., Ph.D., a professor in the Department of Environmental Health Sciences at the Yale School of Public Health. "More studies are needed to identify populations who are susceptible to radiofrequency radiation (RFR) and understand exposure to RFR by different using patterns of cell phones."
Further research is needed to confirm the findings and to better understand the interaction between cell phone radiation and SNPs within specific genes.
The rates of thyroid cancer have been steadily increasing in the United States and in many other parts of the world, Zhang said.
Advertisement
Zhang noted that the study relied on data collected from 2010 to 2011 when smartphones were first being introduced to the market. At the time, only a small proportion of people had smart phones. Therefore, if cell phone use increased the risk of thyroid cancer, it was possibly due to the use of earlier generation cell phones that were more commonly used when the data was collected.
Source-Eurekalert