Older women face an increased risk of frailty with lower and higher vitamin D levels, according to a new study.

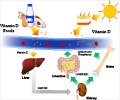
Vitamin D deficiency and frailty are common with aging. Dimensions of frailty, including weakness and slowness are potential outcomes of vitamin D deficiency and many experts have recommended measuring vitamin D levels in older adults and prescribing vitamin D supplementation if levels are less than 30 ng/ml to prevent adverse health outcomes.
This new study however found a U-shaped relationship between vitamin D levels and frailty.
"Vitamin D supplementation has grown in popularity, yet the association between vitamin D status and risk of adverse health outcomes in older adults is uncertain," said Kristine Ensrud, professor of medicine and epidemiology, Minneapolis VA Medical Center and the University of Minnesota and lead author of the study.
"Our study did not find that higher vitamin D status was associated with lower subsequent risks of frailty or death. In fact, higher levels of vitamin D were associated with increased likelihood of frailty."
In this study, researchers measured vitamin D levels and assessed frailty status in a cohort of 6,307 women aged 69 and older. To determine whether lower vitamin D levels were associated with an increased risk of greater frailty status at a later date, 4,551 women classified as non-frail at baseline had frailty status reassessed an average of 4.5 years later.
Advertisement
The study will be published in The Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism (JCEM).
Advertisement