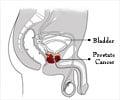
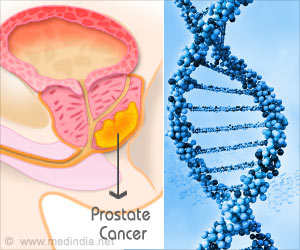
A new research has found that men with a long ring finger could be three times more likely to develop prostate cancer.

Researchers said the 'digit ratio' - the difference in length between ring and index finger - could be used to predict which men could get cancer.
"Digit ratio is a predictor of high PSA levels and the presence of prostate cancer," the Daily Mail quoted the researchers as saying.
"We believe our results present sufficient evidence that a relationship exists between the two," they added.
But Ed Yong, Cancer Research UK's head of health information, said: "Finger length ratios have been linked to all sorts of things before with little evidence that measuring these ratios will ever actually be useful.
"For example, this very small study finds an association between finger length ratio and prostate cancer risk, but tells us nothing about whether the ratio can be used to reliably predict that risk," he added.
Advertisement
Source-ANI



![Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA] Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA]](https://www.medindia.net/images/common/patientinfo/120_100/prostate-specific-antigen.jpg)