People with metabolic syndrome in midlife had heart attacks or strokes 2.3 years earlier than those without these traits.

Early screening for metabolic syndrome opens a window of opportunity learnings from a long-term, population-based study
Go to source).
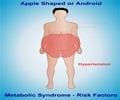
Metabolic Syndrome: Unveiling Unseen Health Risks for Future Heart Health
“This scenario, called metabolic syndrome, is a growing problem in Western populations where people are unknowingly storing up problems for later in life. This is a huge missed opportunity to intervene before heart attacks and strokes that could have been avoided occur,” said study author Dr. Lena Lönnberg of Västmanland County Hospital, Västerås, Sweden. It is estimated that up to 31% of the global population has metabolic syndrome (2✔ ✔Trusted SourceGeographic distribution of metabolic syndrome and its components in the general adult population
Go to source). Previous studies have shown that people with metabolic syndrome are at higher risk of diabetes, heart disease, stroke and premature death (3✔ ✔Trusted Source
A longitudinal study over 40 years to study the metabolic syndrome as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases
Go to source). This study investigated the link between asymptomatic metabolic syndrome in midlife and cardiovascular disease and death up to three decades later.
‘People in their 40s and 50s might have some excess abdominal fat and slightly elevated blood pressure, cholesterol, or glucose levels, yet they generally feel healthy, remain oblivious to the associated health risks, and do not actively seek medical guidance. #unhealthylifestyle #heartattack #stroke #metabolicsyndrome’





The study enrolled 34,269 adults in their 40s and 50s who attended a cardiovascular screening programme in 1990 to 1999 in the Swedish county of Västmanland. Participants went to their primary health care centre for a clinical examination by a nurse, which included measurements of height, weight, blood pressure, total cholesterol, blood glucose, and waist and hip circumference. They also completed a questionnaire about lifestyle habits, previous history of cardiovascular disease and diabetes, and socioeconomic factors such as education.
Metabolic Syndrome Classification Criteria
Individuals were classified as having metabolic syndrome if they had three or more of the following:- waist circumference of 102 cm or above for men and 88 cm or above for women,
- total cholesterol 6.1 mmol/l or above,
- 130 mmHg or higher systolic blood pressure and/or 85 mm Hg or higher diastolic blood pressure,
- fasting plasma glucose 5.6 mmol/l or higher
A total of 5,084 individuals (15%) met the criteria for metabolic syndrome and a control group of 10,168 individuals without metabolic syndrome was identified. Some 47% of participants were women. During a median follow-up of 27 years, 1,317 (26%) participants with metabolic syndrome died compared with 1,904 (19%) controls – meaning that those with metabolic syndrome were 30% more likely to die during follow-up than their counterparts without metabolic syndrome.
Non-fatal cardiovascular events (myocardial infarction and/or stroke) occurred in 1,645 (32%) participants with metabolic syndrome and 2,321 (22%) controls – corresponding to a 35% greater risk of heart attack and stroke in the metabolic syndrome group. The median time to the first non-fatal heart attack or stroke was 16.8 years in the metabolic syndrome group and 19.1 years in the control group – a 2.3 year difference.
Dr. Lönnberg said: “As metabolic syndrome is a cluster of risk factors, the level of each individual component does not have to be severely raised. In fact, most people live with slightly raised levels for many years before having symptoms that lead them to seek health care. Blood pressure was the riskiest component, particularly for women in their 40s, highlighting the value of keeping it under control.”
She concluded: “The results underline the importance of early detection of risk factors through health screening programmes so that preventive actions can be taken to prevent heart attack, stroke and premature death. As a general rule of thumb, even if you feel well, check your blood pressure every year, avoid smoking, keep an eye on your waist circumference and last, but definitely not least, be physically active every day.”
Advertisement
- Early screening for metabolic syndrome opens a window of opportunity learnings from a long-term, population-based study - (https://esc365.escardio.org/ESC-Congress/sessions/8241)
- Geographic distribution of metabolic syndrome and its components in the general adult population - (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0168822722007380)
- A longitudinal study over 40 years to study the metabolic syndrome as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases - (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-82398-8)