Researchers have identified a specialized and distinctive type of microglia with enhanced antioxidant function in stroke mice.
Role of Microglia in Causing Stroke
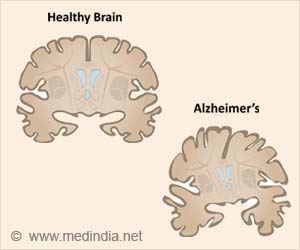
Microglia, the primary immune cells in the central nervous system (CNS), are known to eliminate unwanted germs and debris and remove dying neurons. In this study, the research team classified a new type of microglia with enhanced antioxidant function and markers similar to those of disease-associated microglia (DAM), designated them as stroke-associated microglia (SAM).‘Prdx1-dependent SAM may be a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for protecting microglial function and treating brain I/R injury.’





Through animal experiments, the research team demonstrated that the presence of the typical antioxidant gene, Peroxiredoxin-1 (Prdx1), protects against acute I/R injury and is required for SAM activation and the consequent reduction of microglial cell death and inflammatory responses. In addition, after performing transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) surgery to induce ischemic stroke in mice, the research team found that Prdx1−/− mice were more severely injured by acute I/R injury, as confirmed by TTC staining, neurological deficit scores, motor tests, and the survival rate, indicating that Prdx1 has a protective function.
He adds, “Although this new cluster will require further study, our findings provide a new perspective that Prdx1-mediated microglial heterogeneity is important in ischemic stroke.”
This study has been jointly participated by Wonhyo Lee, a doctoral researcher within the Department of Biological Sciences at UNIST and Sinai Kim, a doctoral researcher within the Department of Life Sciences at Ewha Womans University, as first authors.
Their findings have been published in the August 2022 issue of Redox Biology, a renowned journal in the areas of both health and disease. This study was carried out with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
Advertisement