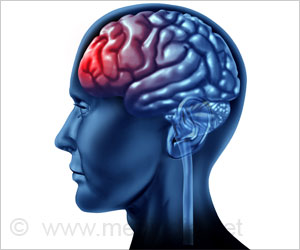
By enhancing the ability of star-shaped glial cells called astrocytes, damage caused by a stroke can be reduced, finds a new study.
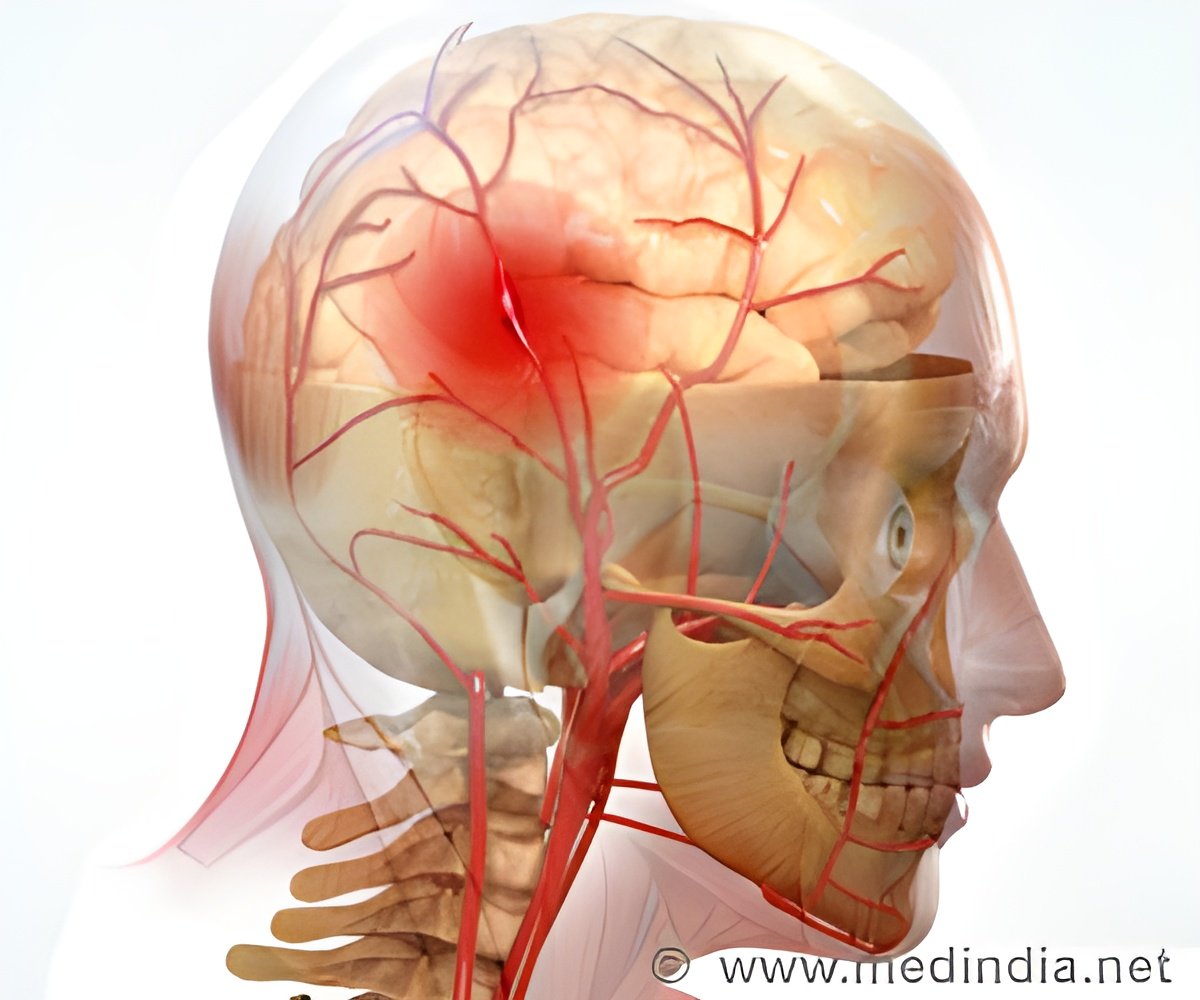
‘Unlike a lot of previous research that focused on trying to protect neurons, but here in this study, the researchers have sought a way to enhance the astrocyte's ability to protect neurons in stroke.’





In a study published today in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, researchers successfully used a new approach that significantly minimized brain damage caused by a stroke in mouse models. The new approach works by targeting hemichannels--pathways that allow for the flow of chemical ions and small molecules--that are expressed by astrocytes, cells that play a protective role for neurons in the brain.When a stroke occurs, these hemichannels open and can leak toxic molecules into the space outside the astrocytes, causing inflammation and damage to neurons.
"Our study definitively confirms that hemichannels are detrimental in stroke, and that we can block them to minimize damage to the brain," said lead author Moises Freitas-Andrade, who conducted this study as a postdoctoral research fellow at UBC and currently is a research fellow at The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. "It's a different approach to stroke treatment. A lot of previous research has focused on trying to protect neurons, but here we sought a way to enhance the astrocyte's ability to protect neurons in stroke."
The researchers focused specifically on ischemic strokes, which occur when the arteries to the brain become narrowed or blocked, resulting in severely reduced blood flow. Ischemic stroke is the most common type, accounting for about 80 percent of all strokes, according to the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada.
For the study, the researchers used a genetic approach that mutated the channel proteins, called connexins, in such a way that blocks the formation of hemichannels. This allows the astrocytes to protect the neurons, significantly reducing the size of the stroke injury in the brain.
Advertisement
The researchers also attempted to mimic "real life" stroke conditions in the study, waiting two hours after the stroke occurred before administering the drug.
Advertisement
The researchers believe the approach could also have potential use for treating other neurodegenerative conditions such as traumatic brain injury and Alzheimer's disease.
The study also involved researchers at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Centre in Seattle and Ghent University in Belgium.
"This research is a great example of how the expertise from laboratories from three different countries could not only identify the importance of these connexin hemichannels but also discover the mechanisms involved and even identify possible avenues for treatment," said study co-author Paul Lampe of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Centre.
"Through the efforts of several labs, we were able to conduct in-depth explorations of channel protein function and its effect on disease treatment and outcome," added Luc Leybaert of Ghent University.
Source-Eurekalert