The tooth provides an excellent source of stem cells, which can be used to make them grow and reduce the burden of artificial tooth replacement.

Growing Tooth Naturally
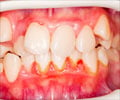
Unlike many other types of human tissue, dental enamel, the outer layer of teeth, doesn’t regrow once it’s damaged. Dentists have to repair cavities and damaged enamel with synthetic materials like ceramics, metals, and resins. If it is missing, then it is replaced with implants or artificial teeth.‘Storing tissue from teeth that are being removed can help dentists to solve oral health problems that develop down the line.’





But scientists are now studying how to grow stem cells into the tooth, which might transform the way dentists treat teeth. It is like imagining a future in which tooth enamel or whole teeth could be replaced.Researchers used stem cells from the dental follicle, the tissue that surrounds teeth, to make the 3D model, which can grow more tooth stem cells in a lab.
"It would be a great advance in the field of stem cells could be used to repair cavities or treat other oral health issues," says senior study author Hugo Vankelecom, PhD at the University of Leuven in Belgium.
In theory, it should be possible for scientists to get dental stem cells from teeth that are naturally lost or surgically removed. Then they could freeze and preserve the cells without losing their ability to grow and regenerate. These cells could also be applied to personalize dental treatments.
Fixing Teeth
Of course, many more lab tests and clinical trials will be needed to see if, one day, dentists can use dental stem cells to fill cavities and fix damaged teeth safely and effectively.Success in the clinic will depend on the ease of collection and biobanking, the cost, and the eventual quality of the repair.
Advertisement
Source-Medindia