Researchers revealed that the risk of cardiovascular events in healthy individuals can be predicted by conducting magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of abdominal aorta.
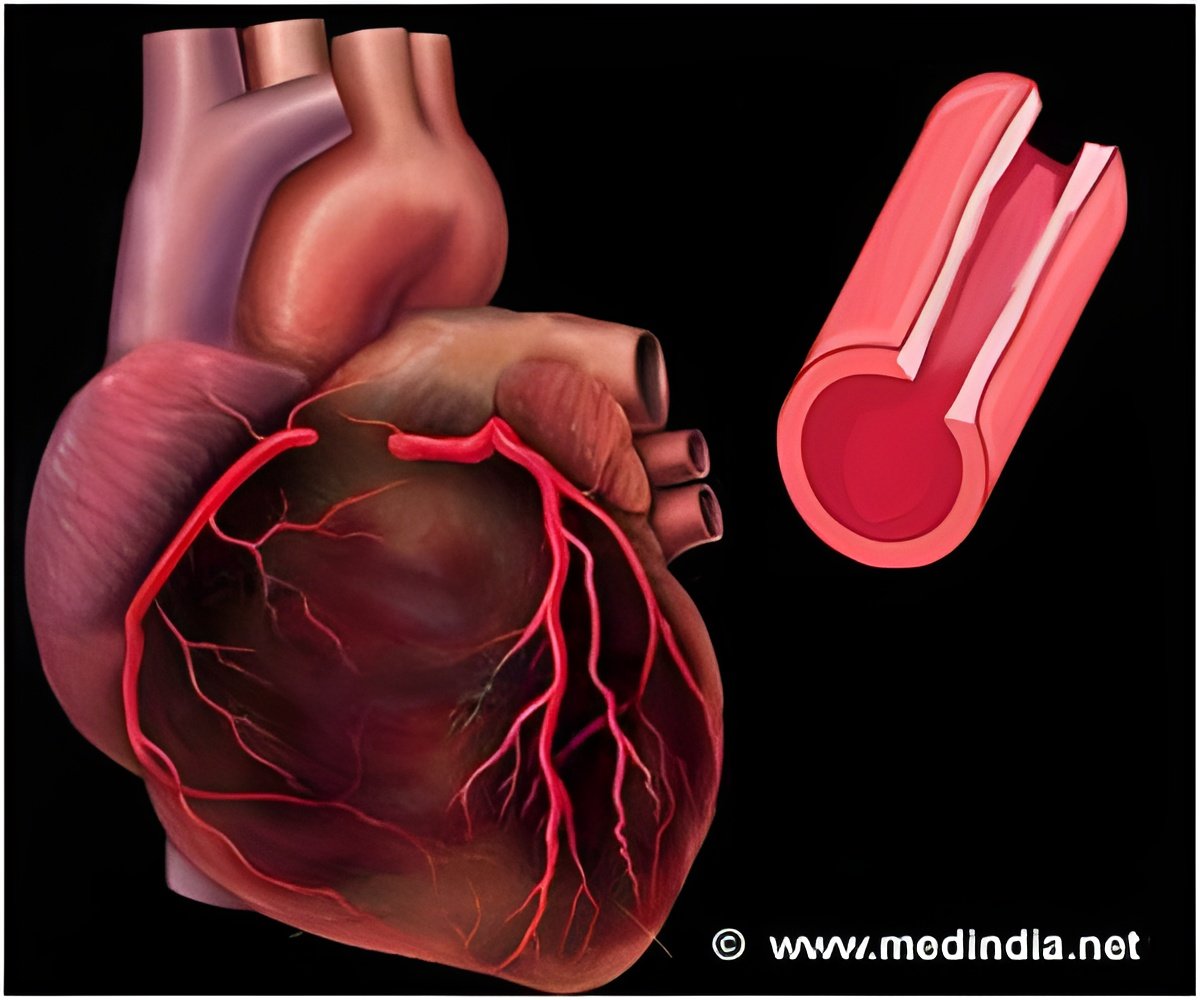
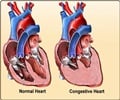
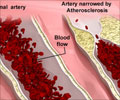
Using MRI, researchers at UT Southwestern were able to measure in thousands of participants very subtle but highly significant differences in two distinct measures of aortic atherosclerosis: aortic plaque buildup and thickness of the aortic walls. Individuals with a thicker aortic wall have almost a twofold higher risk of a future adverse event, said Dr. Amit Khera, associate professor of internal medicine and senior author of the paper.
"Both measurements are predictors of cardiovascular events, but there's an important difference between accumulation of plaque and the thickness of the aortic walls," Dr. Khera said.
"Accumulation of plaque tells us there is increased risk for peripheral vascular occlusion, stroke, and abdominal aortic aneurysms, but not all forms of cardiovascular events, including heart attacks and death from cardiovascular disease," he said. "In contrast, thickening of the aortic walls is more likely to be predictive of all forms of cardiovascular disease."
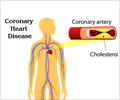
Dr. Christopher Maroules, a resident in diagnostic radiology at UT Southwestern and first author of the new investigation, said, "The relationship between coronary atherosclerosis and adverse cardiovascular events has long been established, but much less is known about atherosclerosis in the aorta."
The size of the aorta also contributes to the ease of using MRI as a predictive tool for cardiovascular events.
Advertisement
In addition, the abdominal aorta is often inadvertently imaged during routine MRI exams of the spine and abdomen.
Advertisement
More than 2,200 healthy adults from the Dallas Heart Study, a groundbreaking multiethnic investigation of cardiovascular disease in Dallas County residents, underwent abdominal aortic MRI as part of the research study.
Although the findings are novel and relevant, Dr. Khera cautioned that they don't necessarily mean that health care providers should use aortic MRIs routinely to screen for cardiovascular event risks.
"While we are not ready to recommend MRI screening for atherosclerosis yet, in patients currently undergoing these exams, findings of a thicker aorta or plaque in the aorta could provide important information," he said.
Other UT Southwestern researchers involved are Dr. Ronald Peshock, assistant dean and professor of radiology and internal medicine; Dr. Eric Rosero, assistant professor of anesthesiology and pain management; and Colby Ayers, faculty associate in the department of clinical science.
Source-Eurekalert