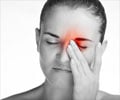
A narrow band of green light worsens a migraine significantly less than all other colors of light and at low intensities green light can even reduce headache pain.
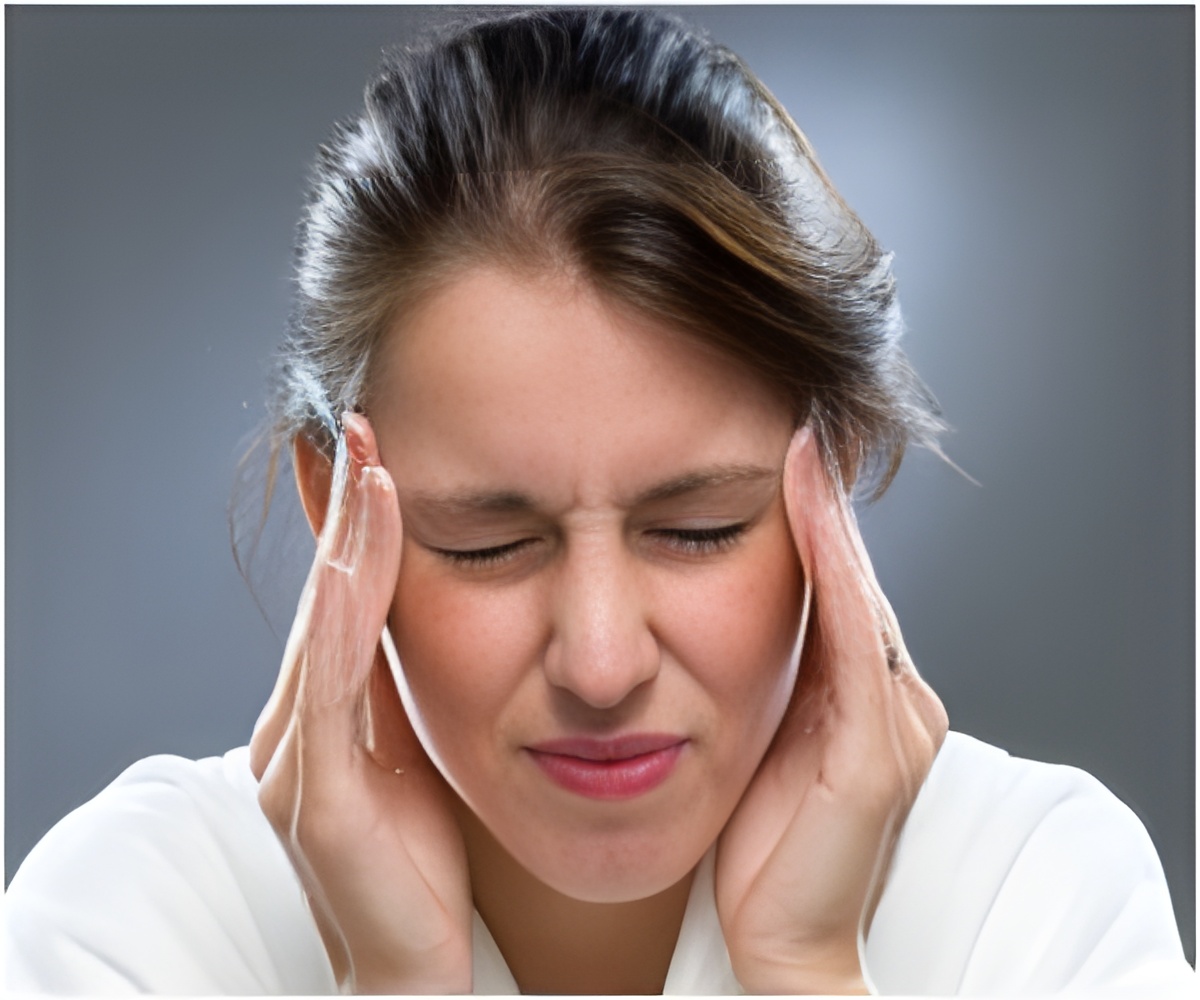

‘Migraine sufferers who were exposed to green light experienced a reduction in the severity of a headache by 20%.’





Five years ago, Burstein and colleagues made the surprising discovery that blue light hurts migraine patients who are blind. This finding prompted the thinking that abnormal sensitivity to light during a migraine could be alleviated by blocking blue light. However, because that study involved only blind patients, who cannot detect all colors of light, Burstein, and his colleagues devised a way to study the effects of different colors of light on headache in patients without visual impairment. In this new study, Burstein and colleagues found that of all light to which migraine sufferers are exposed, a narrow band of green light worsens a migraine significantly less than all other colors of light and that at low intensities green light can even reduce headache pain. The researchers asked patients experiencing acute migraine attacks to report any change in a headache when exposed to different intensities of blue, green, amber and red light. At the high intensity of light - as in a well-lit office - nearly 80 percent of patients reported an intensification of a headache with exposure to all colors but green. Moreover, the researchers found - unexpectedly - that green light even reduced pain by about 20 percent.
To understand exactly why green light causes far less pain to patients with migraines, Burstein and colleagues designed experiments in which they measured the magnitude of the electrical signals generated by the retina (in the eye) and the cortex (in the brain) of these patients in response to each color of light. They found that blue and red lights generated the largest signals in both the retina and the cortex and that green light generated the smallest signals.
Next, applying innovative techniques recently developed by Rodrigo Noseda, PhD, also of BIDMC and Assistant Professor at HMS, they used animal models of a migraine to study neurons in the thalamus, an area of the brain that transmits information about light from the eye to the cortex. These neurons were found to be most responsive to blue light and least responsive to green light, explaining why the migraine brain responds favorably to green light.
"These findings offer real hope to patients with migraines and a promising path forward for researchers and clinicians," said Burstein.
Advertisement
The study is published in the journal Brain.
Advertisement