Scientists have developed a new computer model that is used to guide the design of tiny pillars in a microfluidic device used to detect malignant multiple myeloma cells.
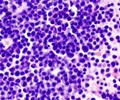
‘Some myeloma cells can leave the bone marrow and enter the blood stream. The presence of these cells, known as clonal circulating plasma cells, or cCPCs, in the blood has been correlated with shorter survival times.’





The device is a type of filter that separates malignant plasma cells from normal ones. It is based on a concept known as microfluidics. The filtering action is due to tiny pillars in the flow channel, designed in a precise way that allows normal blood cells through the filter while capturing the cancerous cCPCs. The scientists who developed this device used a computational model to consider circular-, square- and diamond-shaped pillars of various sizes for their design. Their computer model showed the diamond shape provided a low resistance to flow. They also found by adjusting the diamond shape so that the pillars were longer and more pointed, the filtering action was improved.
Red blood cells are the smallest cells in blood plasma, with diameters in the range of 6-8 microns. White blood cells (WBCs) are bigger, with diameters ranging from 7 to 30 microns. While the cancerous cCPCs are large, with a size of 30-50 microns, the smallest cCPCs are about the same size as the largest WBCs. However, WBCs can deform and squeeze between the tiny pillars. The cCPCs are stiffer and cannot deform this way, so they end up stuck in the filter. Studies were carried out with cultured cancer cells as well as on blood samples from patients with MM.
The amount of cCPCs captured from patients with active MM was much higher than from patients in remission or from healthy individuals. Co-author Lidan You said, "This device shows great potential as a noninvasive method for either early detection or monitoring of MM disease progression."
Source-Eurekalert