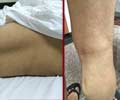
A significant discovery about the cause of age-related muscle atrophy that could lead to new drugs to halt this natural process has been made by scientists in the U.S.
A significant discovery about the cause of age-related muscle atrophy that could lead to new drugs to halt this natural process has been made by scientists in the US.
They have found that free radicals, such as reactive oxygen species, damage mitochondria in muscle cells, leading to cell death and muscle atrophy."Age-related muscle atrophy in skeletal muscle is inevitable. However, we know it can be slowed down or delayed," said Holly Van Remmen, co-author of the study, from the Sam and Ann Barshop Institute for Longevity and Aging Studies at the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio.
"Our goal is to increase our understanding of the basic mechanisms underlying sarcopenia to gain insight that will help us to discover therapeutic interventions to slow or limit this process," Van Remmen added.
To make this discovery, researchers used mice that were genetically manipulated to prevent them from having a protective antioxidant (CuZnSOD).
As a result of not being able to produce this antioxidant, the mice had very high levels of free radicals (reactive oxygen species) and lost muscle mass and function at a much faster rate than normal mice.
Additionally, the muscles of the genetically modified mice were much smaller and weaker than those of normal mice. Scientists believe that these findings mimic effects of the normal aging process in humans, but at an accelerated rate.
Advertisement
Source-ANI
TRI