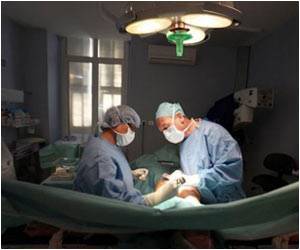
Surgery is the most important treatment for ovarian cancer, and surgeons mainly have to rely on their naked eyes to identify tumor tissue, which is not optimal.
‘A new fluorescent agent, OTL38 enabled surgeons to remove an additional 29 percent of malignant ovarian cancer lesions that could not be identified with naked eyes.’





Background: "Surgery is the most important treatment for ovarian cancer, and surgeons mainly have to rely on their naked eyes to identify tumor tissue, which is not optimal. Near infrared (NIR) fluorescence imaging is a novel technique that may assist the surgeons to improve visualization of tumors during surgery," Vahrmeijer said. How the Study was Conducted: Philip S. Low, from Purdue University, and colleagues developed a new fluorescent agent, OTL38, which is a conjugate of NIR fluorescent dye and a folate analog that binds to folate receptor-alpha (FRα). Vahrmeijer and Jacobus Burggraaf, from the Center for Human Drug Research in the Netherlands, studied OTL38 for the first time in humans. According to Vahrmeijer; FRαis expressed in more than 90 percent of ovarian cancers but in relatively low levels in some normal tissues.
The researchers first conducted a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial to assess the tolerability and pharmacokinetics of OTL38 in 30 healthy volunteers. This allowed them to rapidly determine the optimum dose range and time window for intraoperative imaging in patients with ovarian cancer, Burggraaf explained.
Next, under the supervision of gynecologist Katja Gaarenstroom, the researchers tested OTL38 in 12 patients with ovarian cancer. In addition to measuring tolerability and pharmacokinetics, they studied whether OTL38-guided surgery resulted in the detection of more tumors that were not visible or palpable during surgery.
Results: The researchers found that OTL38 accumulated in FRα-positive tumors and metastases, and enabled the surgeons to remove an additional 29 percent of malignant lesions (confirmed by pathological examination of the resected tumors) that could not be identified with naked eyes and/or palpation.
Advertisement
Author Comment: "In our study, using a tumor-specific fluorescent agent and a dedicated imaging system, a fluorescent signal was detected in tumors in real time during a surgical procedure for ovarian cancer called cytoreduction. This allowed resection of additional tumor lesions that were not visible to the surgeons' naked eyes," added Vahrmeijer. "Although more research is needed, this is hopefully the first step toward improving the surgical outcome of cancer patients."
Advertisement
"Our unique approach using a mixed population of healthy volunteers and patients allowed us to rapidly determine the optimum dose and time window for intraoperative imaging," Burggraaf said. "The success of this study was only possible with the close collaboration between several academic and industry partners."
Limitations: "A limitation of this study is that we cannot say yet what the impact of our findings is on cure or survival of the patients. It is reasonably plausible to assume that if more cancer is removed the survival will be better. However, long-term follow-up studies need to be performed in large patient groups to prove such effects," Vahrmeijer noted.
Source-Eurekalert