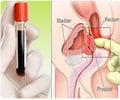
Guangdong Medical College in China researchers have demonstrated the potential of a new, non-invasive method to screen for prostate cancer, a common type of cancer in men worldwide.
If the technique proves safe and effective in clinical trials, it may become a new method available to patients and their doctors, helping to improve the early detection and diagnosis of this type of cancer, said Li.
"The results demonstrate that label-free serum SERS analysis combined with SVM diagnostic algorithm has great potential for non-invasive prostate cancer screening," said Li. "Compared to traditional screening methods, this method has the advantages of being non-invasive, highly sensitive and very simple for prostate cancer screening."
A COMMON CAUSE OF CANCER
According to the World Health Organization, prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in men worldwide and a leading cause of cancer-related death. Every year, there are about 899,000 new cases and 260,000 mortalities, comprising 6 percent of all cancer deaths globally. About 1 in every 6 men will develop prostate cancer over their lifetimes.
While a simple blood test for elevated levels of a protein marker known as prostate specific antigen (PSA) has been used for years to screen for early cases of prostate cancer, the test is far from perfect because the elevated PSA levels can be caused by many things unrelated to cancer. This contributes to over-diagnosis, uncomfortable tissue biopsies and other unnecessary treatment, which can be costly and carry significant side effects. Because of this, the U.S. Preventative Services Task Force now recommends against PSA-based screening for prostate cancer.
Advertisement
The challenge, he said, was that these changes were, if anything, too subtle. The signal differences between the serum samples taken from the 68 healthy volunteers and the 93 people with prostate cancer were too tiny to detect. So to accurately distinguish between these samples, Li's group employed a powerful spectral data processing algorithm, support vector machine (SVM), which effectively showed the difference.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert

![Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA] & Prostate Cancer Diagnosis Prostate Specific Antigen [PSA] & Prostate Cancer Diagnosis](https://images.medindia.net/patientinfo/120_100/prostate-specific-antigen.jpg)