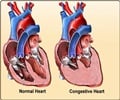
Researchers have developed a new mode of emergency anticoagulant treatment for patients with acute myocardial infarction.
The first is based on heparin (traditional treatment), the other on a more specific anticoagulant, bivalirudin. One of the main drawbacks of these anticoagulant treatments is the risk of associated haemorrhage. "By dilating the arteries, we also thin the blood, with the risk of uncontrolled bleeding if haemorrhage occurs," explains Philippe-Gabriel Steg. After 30 days of monitoring, bivalirudin reduced the risk of death or serious bleeding by 8.5 to 5.1% and the risk of death, myocardial infarction or major bleed by 9.2 to 6.6%, compared with the strategy using heparin. This benefit was mainly linked to the reduction in serious bleeding, at the cost of an increased risk of stent thrombosis . "The benefits are robust and consistent for all sub-groups tested, and in particular, consistent regardless of the type of oral anti-clotting treatment or route of arterial access used for angioplasty (via the radial or femoral artery)," explains Philippe-Gabriel Steg. These results open up the way to using bivalirudin as an anticoagulant at the pre-hospital phase of myocardial infarction in patients being urgently transferred. They represent progress in the treatment of myocardial infarction that can be immediately used.
Source-Eurekalert