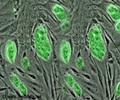
A new model that sheds light on how tissue organizes into organs and layers during embryonic development has been developed by a group of researchers.
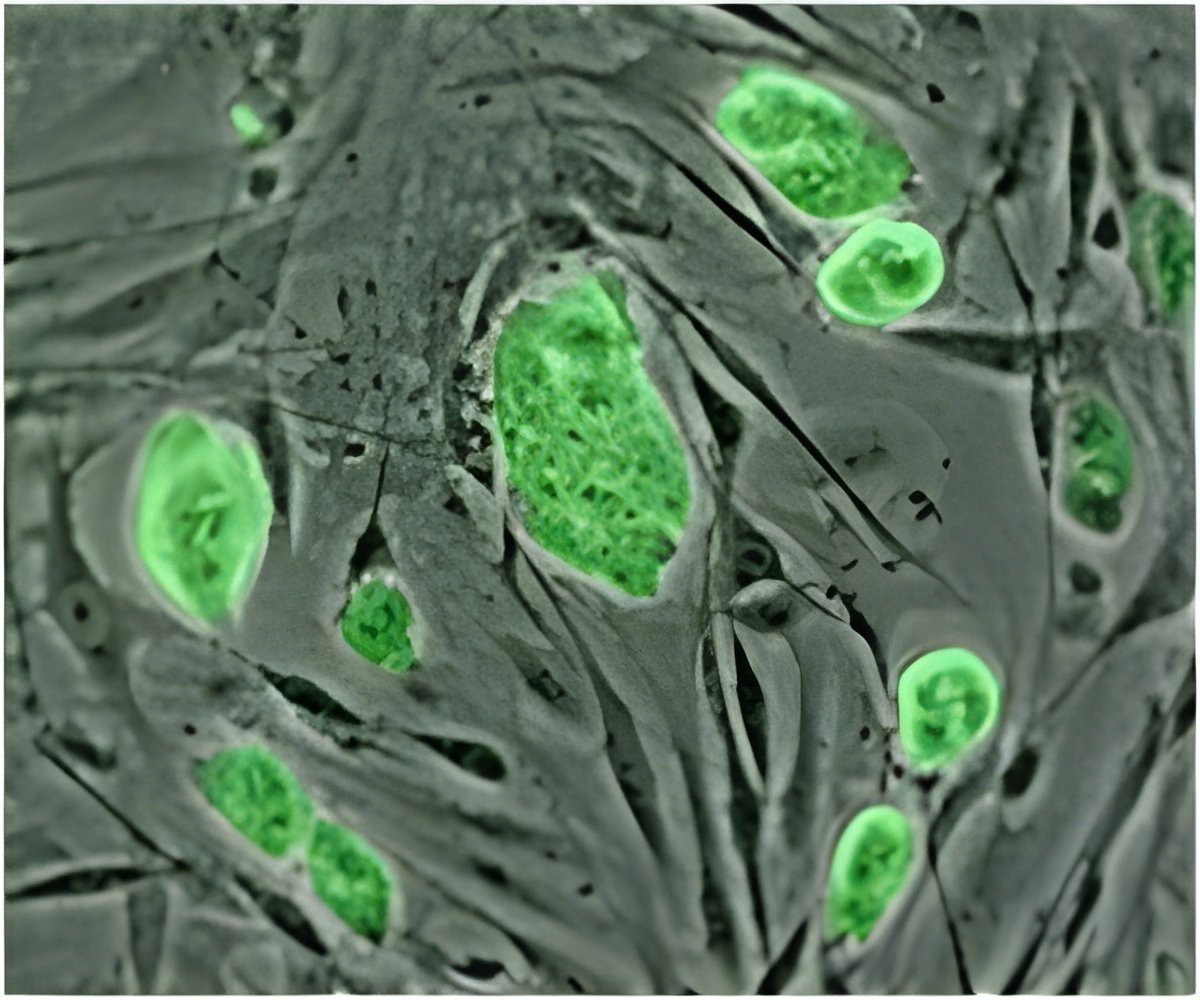
Central to their work was the question of whether embryonic tissue behaves more like a solid or a liquid—and why.
"We found that embryonic tissue was viscoelastic, meaning that it behaved like a liquid, if you pushed on it slowly, but like a solid, if you pushed on it quickly," says Manning, who co-wrote the article with Eva-Maria Schoetz, assistant professor of biology and physics at the University of California, San Diego; and Marcos Lanio and Jared Talbot, both researchers in Princeton University's Lewis-Sigler Institute for Integrative Genomics. "A mixture of cornstarch and water also behaves that way."
Manning and her team found that viscoelasticity was the result of "glassy dynamics" in cells, caused by overcrowding. They discovered that cells within embryonic tissue were packed so tightly that they rarely moved—and when they did so, they expended considerable energy to squeeze past their neighbors.
She compares this behavior to riding on a subway. "If you're on a subway train that's not very crowded, it's easy to move toward the exit and get off the train," says Manning, an expert in theoretical soft condensed matter and biological physics. "But as more people get on the train, it takes longer to pick your way past them and exit. Sometimes, if the train is jam-packed, you miss your stop completely because you can't move at all."Experimental and simulation data from Manning's experiment, in which two "droplets" of tissue join together, in a fluid-like manner, to form a single tissue.Using state-of-the-art imaging and image analysis techniques, Manning and her team saw that each cell was crowded by what she calls a "cage of neighbors." A simple active-matter model, which they created, has enabled them to reproduce data and make predictions about how certain changes and mutations affect embryonic development.
"This is exciting because if cells slow down or generate more sticky molecules, the tissue can turn into a solid," says Manning, adding that such alterations can trigger malformations or congenital disease. "Our results provide a framework for understanding these changes."
Advertisement
Advertisement