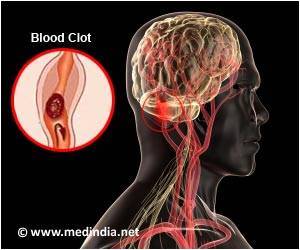
Oral anticoagulant drugs that treat and prevent blood clots offer a much-needed alternative to warfarin, which has been used for more than six decades and has serious shortcomings.
Warfarin has been the drug of choice to control blood clots in a variety of patients, including people with certain types of irregular heartbeats, people with prosthetic heart valves, and people who have suffered heart attacks. Unfortunately, warfarin has serious side-effects, requires frequent monitoring to reduce the risk of bleeding, and has interactions with multiple drugs and foods. New oral anticoagulant drugs—Apixaban, Dabigatran, and Rivaroxaban —offer safer alternatives to warfarin, but there are currently no markers for measuring activity levels of the drugs and there are no antidotes to reverse or neutralize their effects.
Aida Lai, MBChB, of the North Bristol NHS Trust in the UK, and her colleagues searched the medical literature and analysed studies published between January 2000 and January 2014 that reported on the use of new oral anticoagulant drugs. "As these drugs are still relatively new in the market, knowledge about how they work and their associated bleeding risks are still limited in the medical and surgical community," said Dr Lai.
"Our review covers recommendation for the discontinuation of new oral anticoagulant drugs before surgical procedures and resuming of these drugs after procedures." The review also notes that because the drugs are eliminated by the kidneys, they require dose reductions dependent on a patient's kidney function. Also, new oral anticoagulants are not recommended in patients with severe liver dysfunction. And because the three drugs have somewhat different properties, one of the drugs may be better suited to a particular patient than the others.
"It is anticipated that in the near future these drugs would replace warfarin to a large extent," said Dr Lai. "Therefore our article is highly relevant to surgeons and any medical professional treating patients on these drugs."
Source-Eurekalert