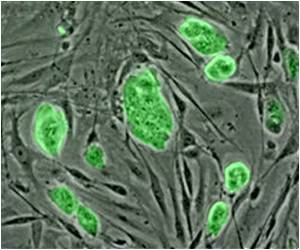
BMI1 protein is a central control switch within the adult stem cells of many tissues and helps scientists develop tissues to replace damaged organs in the human body.

Klein's research group now has shown that BMI1 plays another role in ensuring that the process of development unfolds normally.
The hallmarks of all stem cells are that they are immature, they keep dividing to replenish their numbers almost indefinitely, and they generate new specialized cells to function in the tissues in which they reside, a process called cell differentiation.
Pushed in one direction, the BMI1 switch enables normal stem cells to divide and renew their own numbers. Thrown in the other direction, it keeps cell proliferation in check.
But now, Klein's research team has shown that BMI1 also keeps this stock of stem cells from spinning off daughter cells that mature into the wrong type of specialized cell in the wrong place.
The new discovery suggests that manipulating BMI1, along with other regulatory molecules, might one day be among the steps included in molecular recipes to turn specialized cell development on and off to create new cell-based treatments for tissues lost to injury, disease or aging, Klein said.
Advertisement
The study has been published in Nature Cell Biology.
Advertisement