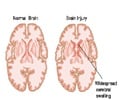
Researchers found that targeting overactive immune cells in the brain with an experimental drug could limit brain cell loss and reverse cognitive and motor difficulties caused by traumatic brain injury (TBI). The findings suggest a potential new treatment for TBI and possibly other brain injuries.
‘Both human and animal brains have specialized immune cells, called microglia, that protect against bacteria or viruses that enter the brain.’





The UMSOM scientists administered a CSF-1R inhibitor for one week to mice beginning one month after TBI- a time at which animals have brain inflammation and neurological deficits. The researchers found the drug depleted more than 95 percent of the brain's overactive immune cells (microglia) that are known to cause neurotoxic inflammation. Several weeks following the treatment, the cells had regenerated and the new cells were more similar to normal microglia, with less inflammatory features.More importantly, the mice recovered markedly better than the control group that didn't receive treatment, showing less loss of tissue and neurons with significantly better motor and cognitive performance.
"We were surprised to see that the extent to which such late treatment could reverse the inflammatory state and the cognitive effects of experimental TBI," said study co-author Rebecca Henry, PhD, Research Associate in Anesthesiology at UMSOM. "This was a proof of concept study that depletion and subsequent repopulation of microglia cells after injury has a strong protective effect, but we clearly need more research to better understand this process before clinical translation."
Both human and animal brains have specialized immune cells, called microglia, that protect against bacteria or viruses that enter the brain.
Evidence from previous clinical studies has shown an increase in microglia activation in patients who have suffered a moderate or severe traumatic brain injury. These changes appear to be correlated with neurological deficits in such patients, including cognitive function.
Advertisement
The next step for the researchers is to isolate the microglia cells and use RNA resequencing techniques to learn more about which genes are driving inflammation and overactivation in order to better understand the mechanism identified in this study.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert