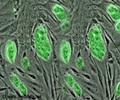
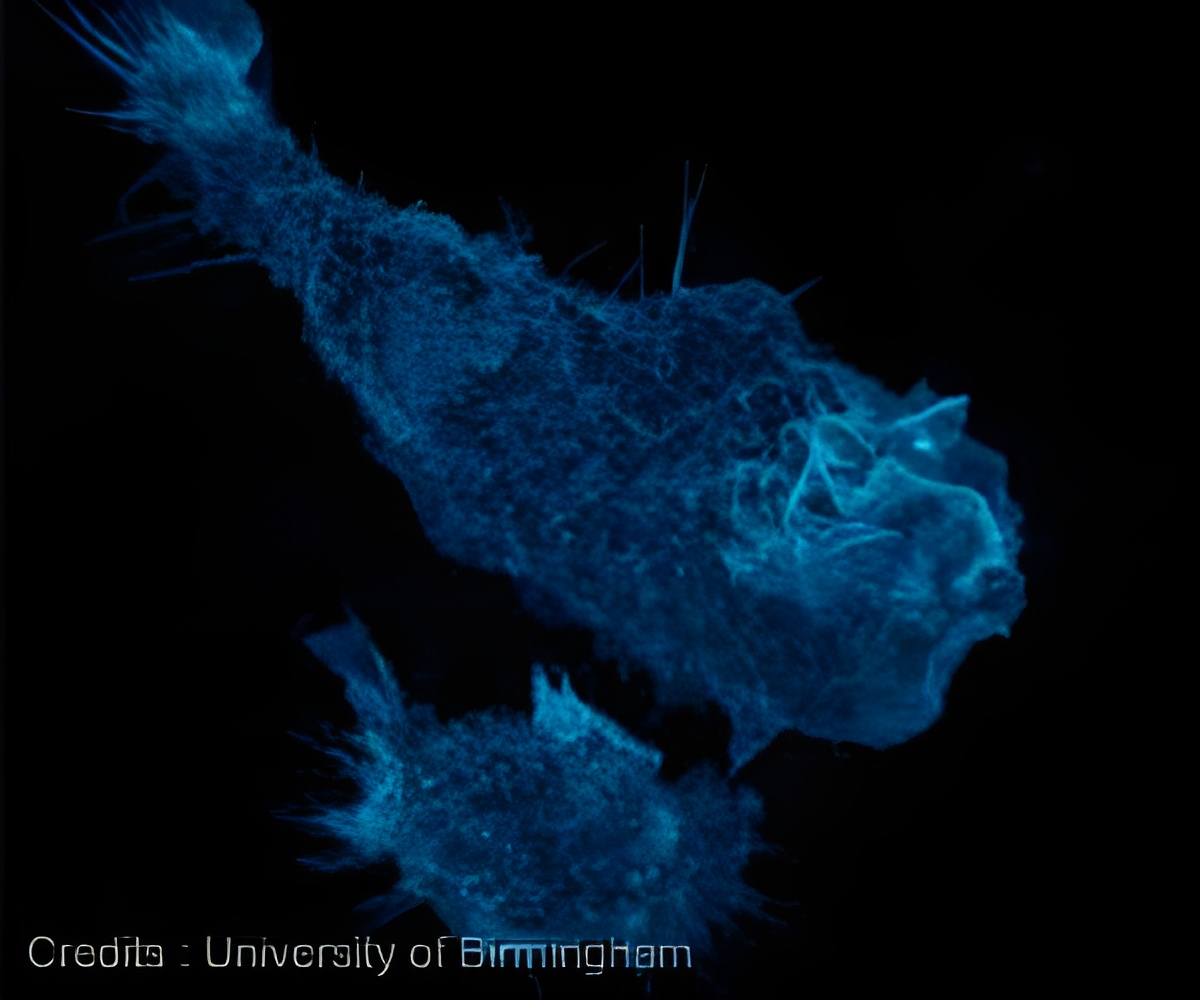
Macrophage, a white blood cell identifies the invading bacteria or fungus, 'eats it', destroys it and then alerts the rest of the immune system.
‘Blocking a molecule called ERK5 can help prevent a deadly fungal infection from spreading to the brain.’





Professor Robin May, Director of the Institute of Microbiology & Infection at the University of Birmingham, said: "When an infection starts, the first white blood cell to respond is called a macrophage. This identifies the invading bacteria or fungus, 'eats it', destroys it and then alerts the rest of the immune system."However, in the case of some diseases like Cryptococcosis, the invading organism has evolved to be able to survive inside that white blood cell and then use them like a public transport system to help move around the body.
"We know that many white blood cells overcome this by throwing those hijackers out, using a mechanism called 'vomocytosis'. However, we don't know how vomocytosis is controlled.
"There are many diseases, not only Cryptococcosis, in which pathogens - bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites that can cause disease - survive by deliberately hijacking the immune system in this way.
"This research aimed to identify the mechanism that allows white blood cells to recognise and expel these hijackers.
Advertisement
The findings of the study, carried out in collaboration with the Universities of Sheffield, Dundee, and Manchester in the UK, as well as the University of Leuven in Belgium and Harvard Medical School in the US, were published in Science Advances.
Advertisement
Professor May continues: "We found that by blocking ERK5 in zebrafish, we were able to increase vomocytosis rates in their white blood cells and so prevent a deadly fungal infection from spreading to the brain.
"As a consequence of this research we have a greater understanding of a really subtle and new aspect of the human immune system.
"Longer term, our hope is that we will be able to develop therapies that target this process, such as drugs that would be able to limit an infection and prevent it from spreading from the initial site of attack.
"We would also now like to broaden this research to see how much this process may play a similar role in other major human diseases."
Source-Eurekalert