Scientists discover molecular mechanisms to selectively inhibit human immunoproteasome to prevent autoimmune diseases.
‘Autoimmune diseases can be prevented by developing new drugs that target inhibition of immunoproteasome.’





Our immune system protects us from dangerous intruders. However, in order to recognize that something has gone awry in an afflicted cell, information on the proteins currently present inside the cell is required. This important task is handled by the immunoproteasome, a large, cylindrical protein complex.It decomposes proteins and ensures that the fragments are presented at the surface of the cell. These cleavage products are regularly checked by the immune system and when it identifies one of these fragments as "foreign", from a virus for example, it destroys the cell.
A Helper Out of Control
Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes or multiple sclerosis can result from overactivity of the immunoproteasome. Since this leads to undesired inflammation reactions that mistakenly attack healthy tissue, scientists are trying to develop drugs that inhibit the immunoproteasome.
But it is particularly important to find a compound that blocks solely the immunoproteasome and not the so-called constitutive proteasome, which has a different task in the cell: It is responsible for recycling defective or superfluous proteins and differs from immunoproteasomes merely in its catalytic subunits.
Advertisement
The Path to a Selective Agent
Advertisement
"In the past, we knew that certain agents attack immunoproteasomes stronger than constitutive proteasomes, but we did not understand why," explains Groll. "Knowledge about how various inhibitors target both proteasome types, will facilitate the development of compounds with higher selectivity and efficacy."
The researchers were also able to reveal the reason why many inhibitors bind much better to human immunoproteasomes than to the immunoproteasome of mice: "A single amino acid, in which the two species differ, causes the active agent to 'jam' in mice, while it can easily dock to the human protein complex. This is important for the pharmaceutical industry, because it suggests that certain inhibitors should not be tested on mice," says Huber.
A human protein in yeast - long-term efforts bear fruits
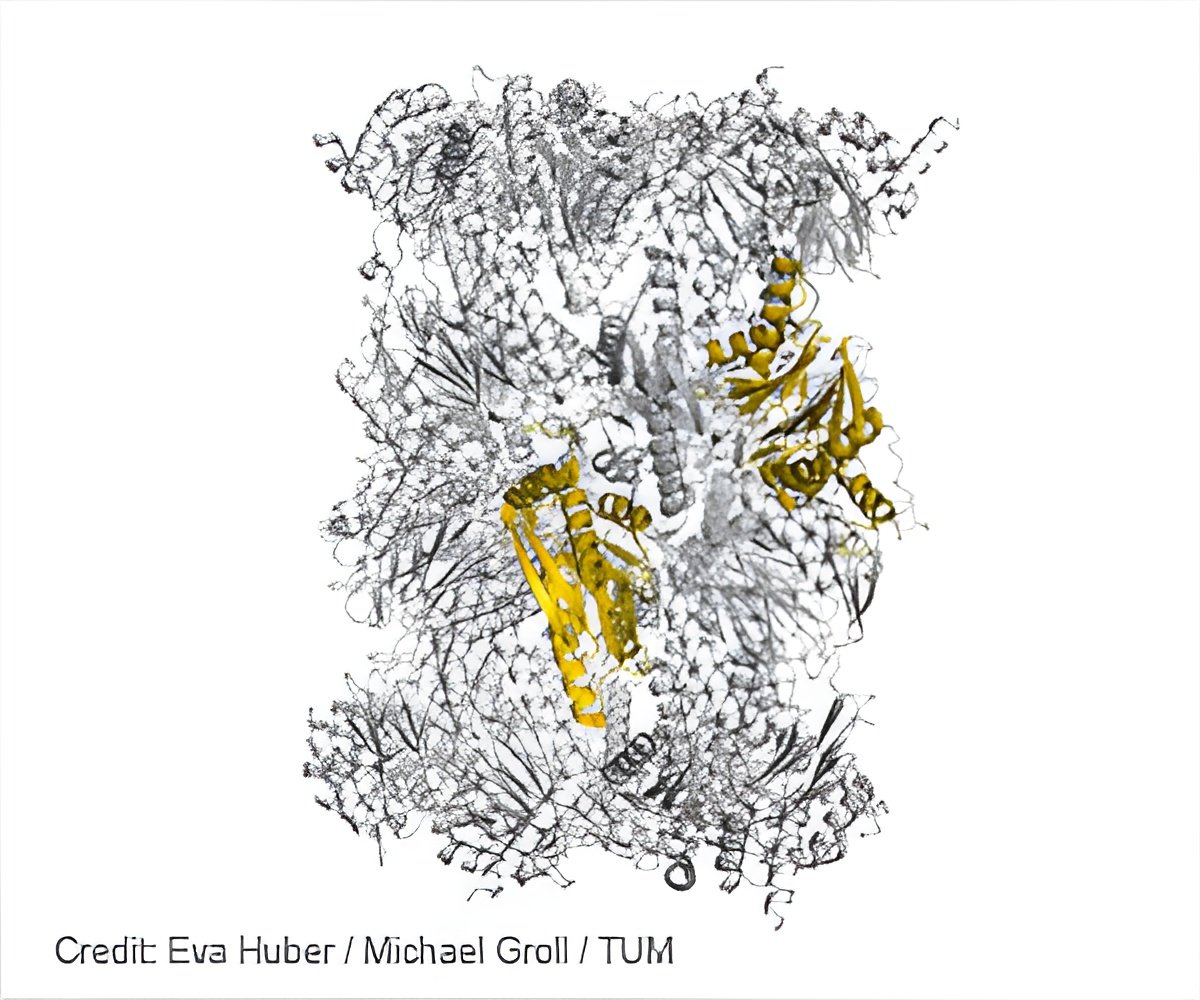
In their work, the researchers present a new methodology for structurally investigating human proteasomes, which are difficult to isolate: To this end, they inserted the sequences of the human proteasome types responsible for inhibitor binding into the proteasome of yeast cells - a technology that builds on attempts to incorporate entire immunoproteasome subunits into the yeast proteasome 23 years ago.
"The resulting chimeric proteins, comprising yeast and human sequences can be easily produced in large quantities. And astonishingly they are structurally similar to natural immunoproteasomes," says Heinemeyer. "Thus, we have created a model in which inhibitors can be investigated very well."
An inhibitor whose core structure was also subject of the research by Prof. Groll's team is already being tested in clinical trials. The newly acquired knowledge will open the door to further optimize drug candidates in the future.
Source-Eurekalert