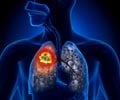
Randomized, phase 3 trials analyzing nivolumab with docetaxel in previously treated Non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC) patients showed improved survival rates in nivolumab group.
‘Nivolumab improves long-term overall survival rate and offers more progression-free survival benefit compared to docetaxel for patients with NSCLC.’
Read More..




Nivolumab, a programmed death-1 inhibitor, was approved in 2015 for patients with previously treated advanced NSCLC based on two randomized phase three trials, CheckMate 017 and CheckMate 057, which demonstrated improved overall survival compared to docetaxel. Read More..
In CheckMate 017 and 057, 854 patients with advanced NSCLC, ECOG performance status 0 to 1, and progression during or after first-line platinum-based chemotherapy, were randomized 1:1 to nivolumab or docetaxel until progression or unacceptable toxicity. After completion of the primary analyses, patients in the docetaxel arm no longer receiving benefit could cross over to receive nivolumab. The researchers set overall survival as the primary endpoint for both studies.
At five-year follow-up, 50 nivolumab patients and nine docetaxel patients were alive. Baseline characteristics of five-year survivors in both arms were similar to the overall population and patients who survived less than one year, except for a higher percentage of patients with ECOG PS 0 or tumor programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression greater than one percent on nivolumab and ECOG PS 0 and Stage IIIB NSCLC on docetaxel.
Nivolumab continued to show long-term overall survival and progression-free survival benefit compared to docetaxel with five-year survival rates of 13.4 percent vs 2.6 percent and progression-free survival rates 8.0 percent compared to 0 percent. The overall survival benefit with nivolumab compared with docetaxel was observed across subgroups, including patients with tumor PD-L1 expression <1 percent.
No new safety signals were observed with longer follow-up. Between three- and five-year's follow-up, eight of the 31 (26 percent) nivolumab-treated patients reported a treatment-related adverse event, one (3 percent) grade three-four. The most common select adverse events (events with a potential immunological cause) were related to skin, in 4 (13 percent) patients, none of which were grade three or four.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert