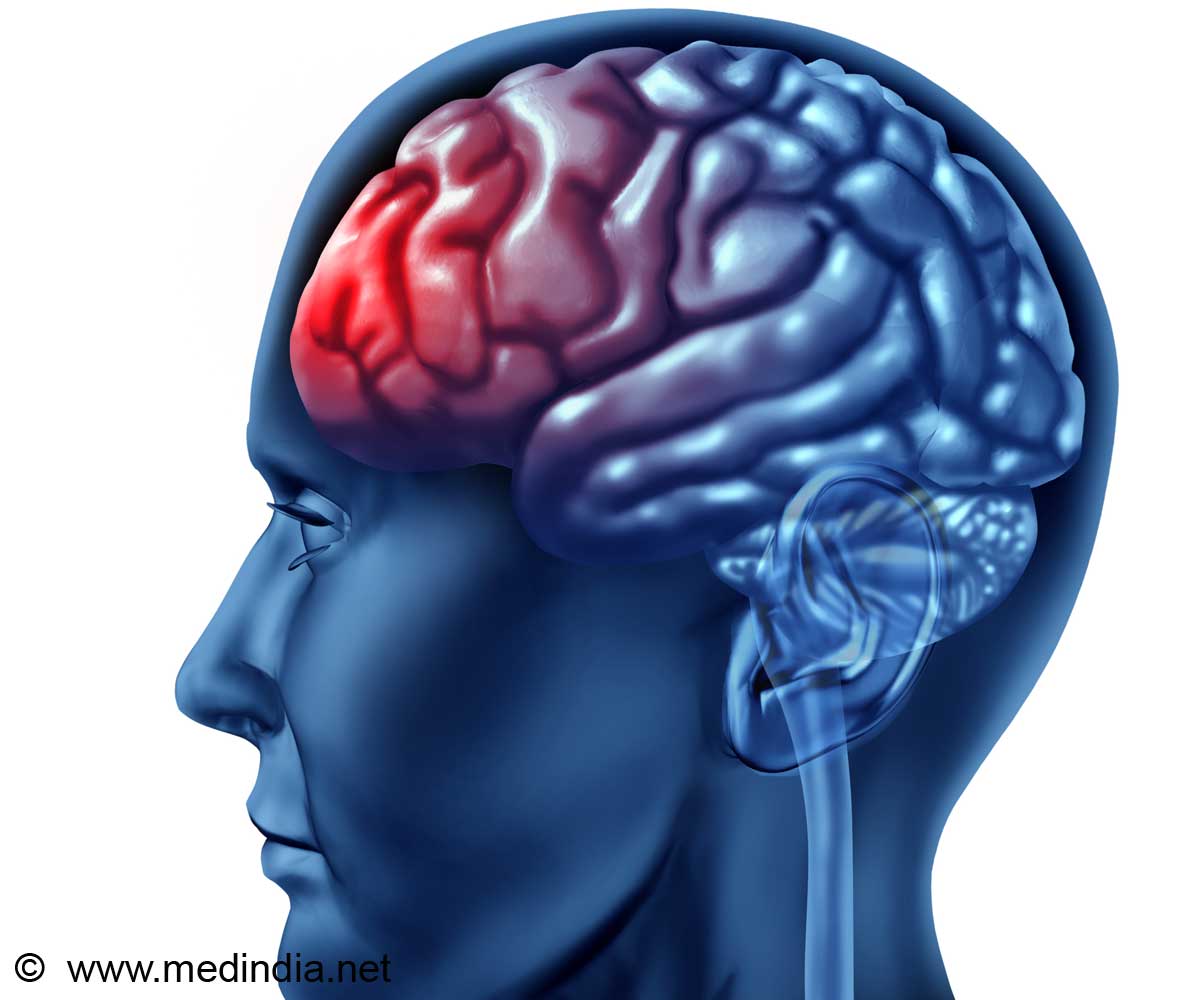
Bioengineering technique offers innovative solutions for diagnosing and repairing brain damage caused by a traumatic injury.
Bioengineering technique offers innovative solutions for diagnosing and repairing brain damage caused by a traumatic injury. These new techniques are presented in a special issue of
Journal of Neurotrauma.
The issue captures the broad scope of current and future diagnostic and therapeutic strategies being developed based on novel biomaterials, innovative applications of biomechanics, and advanced simulation and computational technology. Guest Editors Michelle C. LaPlaca, PhD, Associate Professor of Biomedical Engineering, Georgia Tech College of Engineering, and David F. Meaney, PhD, Associate Director, Penn Center for Brain Injury and Repair, and Professor and Chair, Department of Bioengineering, University of Pennsylvania, have compiled a fascinating collection of articles that describe leading research in the areas of three-dimensional cell and tissue preparations designed to study the effects of brain trauma and to stimulate nerve regeneration, computer modeling, and novel imaging and analytical techniques being applied to advance neurotrauma research and patient care.
Original research articles featured in this issue of Journal of Neurotrauma include "A Detailed Viscoelastic Characterization of the P17 and Adult Rat Brain," by Benjamin Elkin et al.; "Survival Risk Assessment for Primary Blast Exposures to the Head," by Karin Rafaels and colleagues; and "Toward a Convergence of Regenerative Medicine, Rehabilitation, and Neuroprosthetics," by Shyam Aravamudhan et al.
"The Journal is pleased to publish this issue which addresses many of the bioengineering advances being made in the field of central nervous system injury. Further, this compendium of manuscripts emphasizes the important, yet underappreciated, fact that biomechanical-induced change distinguishes CNS trauma from all other CNS disorders," says John T. Povlishock, PhD, Editor-in-Chief of
Journal of Neurotrauma and Professor, VCU Neuroscience Center, Medical College of Virginia, Richmond.
Source-Eurekalert