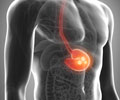
New study sheds light on the development of stomach cancer therapies. Scientists have uncovered further information about the underlying mechanisms for gastric cancer, providing hope of potential new treatments in the future.
‘New study sheds light on the development of gastric cancer therapies. Scientists have uncovered further information about the underlying mechanisms for gastric cancer, providing hope of potential new treatments in the future.’
Read More..




The team, at the University's European Cancer Stem Cell Research Institute, found they could stop gastric cells dividing and growing by deleting a particular cell-surface receptor implicated in the function of stem cells.Read More..
Dr. Toby Phesse, Cardiff University, said: "The prognosis of gastric cancer is very poor, with very few treatment options available to patients, and thus we desperately need new clinical treatments for this disease.
"Some patients with gastric cancer have mutations in genes that are involved in the regulation of Wnt - a cell signaling pathway involved in cell division. It drives the development of cancer and the spread of cancers throughout the body.
"We also see an increase in some of the Fzd receptors, which transmit Wnt signaling, and this is linked to poor prognosis in gastric cancer.
"Despite this evidence, there is limited research investigating the potential of targeting Wnt receptors as a treatment for gastric cancers. We aimed to understand the implications of inhibiting Wnt by targeting Fzd receptors and whether this could be used as an effective treatment."
Advertisement
Dr. Phesse added: "This information gives us a potential new therapeutic route for gastric cancers, as we could target Fzd7 and consequently inhibit Wnt signaling and tumor growth. In fact, Vantictumab is a drug known to inhibit several Fzd receptors, including Fzd7, and is currently in clinical trials for the treatment of other cancers - like pancreatic, lung and breast.
Advertisement
"This research extends the scope of patients that may benefit from this therapy, to now include gastric cancer patients, and future work will establish if we can proceed with clinical trials targeting Wnt receptors for this devastating disease."
Source-Eurekalert