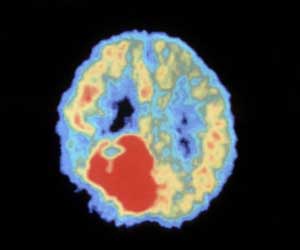
A well-established optics technique can reveal exactly where brain tumors are, producing images in less than a minute, unlike conventional methods.
‘A well-established optics technique can reveal exactly where brain tumors are, producing images in less than a minute, unlike conventional methods that can take a whole day.’





Pathologists typically use staining methods, in which chemicals like hematoxylin and eosin turn different tissue components blue and red, revealing its structure and whether there are any tumor cells. But for a definitive diagnosis this process can take up to 24 hours, which means surgeons may not realize some cancerous tissue has escaped from their attention until after surgery -- requiring a second operation and more risk. But with the new technique, the researchers don't use any labeling or staining at all. Instead, they fire short, 200-femtosecond-long laser pulses into the tissue, and when three photons converge at the same time and place, the photons interact with the nonlinear optical properties of the tissue. Through well-known phenomena in optics called second and third harmonic generation, these interactions produce a single photon.
The key is that the incoming and outgoing photons have different wavelengths. The incoming photons are at 1200 nanometers, long enough to penetrate deep into the tissue. The single photon that is produced, however, is at 600 or 400 nanometers, depending on if it's second or third harmonic generation. The shorter wavelengths mean the photon can scatter in the tissue. The scattered photon thus contains information about the tissue, and when it reaches a detector, in this case a high-sensitivity GaAsP photomultiplier tube, it reveals what the tissue looks like inside.
While other researchers have exploited this technique for other applications -- to make images of insects and fish embryos, for example -- this is the first time anyone has used it to analyze glial brain tumors. These tumors are particularly deadly because it's hard to get rid of tumor cells by surgery, irradiation, and chemotherapy without substantial collateral damage to the surrounding brain tissue.
The researchers tested their method on samples of glial brain tumors from humans, finding that the histological detail in these images was as good -- if not better -- than those made with conventional staining techniques. They were able to make most images in under a minute. The smaller ones took less than a second, while larger images of a few square millimeters took five minutes. "This makes it possible to do it in real time in the operating room," Groot said.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert